Energy Sources: A Comprehensive Guide to Conventional and Non-Conventional Energy
What Makes a Good Energy Source?
Energy is the fundamental capacity to perform work, and selecting the right energy source is crucial for sustainable development. A good energy source must provide sufficient useful energy at a steady rate over extended periods while meeting several critical criteria.
The ideal energy source should release substantial heat during combustion or conversion, produce minimal smoke and pollutants, and remain readily available for consistent use. Additionally, it must be safe and convenient to use, perform large amounts of work per unit volume or mass, allow for easy storage and transportation, and most importantly, remain economically viable for widespread adoption.
Classification of Energy Sources: Renewable vs Non-Renewable
Energy sources fall into two primary categories based on their availability and regeneration capacity. Renewable energy sources are inexhaustible and continuously supplied by nature, including solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, ocean thermal energy, and geothermal energy. These sources regenerate naturally and can be used indefinitely without depletion.
Conversely, non-renewable energy sources are exhaustible and cannot be replenished once consumed. These include fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which took millions of years to form from prehistoric plant and animal remains buried under intense pressure and heat. While these conventional sources currently meet the majority of global energy demands, their finite nature necessitates the development of sustainable alternatives.
Fossil Fuels: The Foundation of Industrial Energy
Fossil fuels remain the backbone of global energy production, formed through the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter over millions of years. Coal, the most abundant fossil fuel, consists primarily of carbon and serves as the principal heat source for electricity generation and as a reducing agent in steel production. Different coal grades offer varying energy outputs: lignite (28-30% carbon) and bituminous coal (78-87% carbon) burn faster but release more pollutants, while anthracite, with the highest carbon content, burns slowly and delivers maximum energy with minimal smoke.
Petroleum, refined through fractional distillation, yields multiple useful components including gasoline, diesel, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Natural gas, typically found near oil deposits, burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, producing less carbon dioxide and serving as compressed natural gas (CNG) for vehicles. Thermal power plants harness these fossil fuels by burning them to heat water, creating steam that drives turbines to generate electricity—a process more efficient than transporting raw fuel over long distances.
Harnessing Renewable Energy: Solar Technology
Solar energy represents one of the most promising renewable sources, utilizing both direct and indirect collection methods. Solar heating devices, including box-type and spherical reflector cookers, employ the greenhouse effect principle where glass covers trap infrared radiation while allowing shorter wavelengths to enter. Box-type solar cookers can achieve temperatures of 100-140°C, suitable for slow cooking, while spherical reflector designs using concave or parabolic mirrors can reach higher temperatures for frying and baking.
Solar cells, or photovoltaic cells, directly convert sunlight into electricity through semiconductor technology. A typical silicon solar cell generates 0.5-1V and produces approximately 0.7W of electricity. When arranged in panels with silver interconnections for minimal resistance, these cells power everything from satellites to irrigation pumps. Despite high initial costs due to special-grade silicon and silver components, solar panels offer maintenance-free operation, work without focusing devices, and can be deployed in remote locations where traditional power transmission proves uneconomical.
Wind and Ocean Energy Systems
Wind energy harnesses kinetic energy from moving air masses caused by differential solar heating between Earth's equatorial and polar regions. Modern wind turbines convert this motion into electricity, though the technology faces challenges including intermittent availability, location-specific wind patterns, and the inability to store wind energy directly. Wind farms aggregate multiple turbines to generate substantial electricity, particularly effective in areas with consistent, strong winds.
Ocean energy encompasses multiple technologies: tidal energy utilizes gravitational forces from the moon to drive turbines in specially constructed dams; wave energy captures kinetic energy from wind-driven sea waves through floating generators or compressed air systems; and ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) exploits temperature differences between surface and deep waters to vaporize working fluids like ammonia, driving turbines for electricity generation. Each ocean energy system offers renewable, pollution-free power but requires specific geographical conditions and significant infrastructure investment.
Nuclear Energy: Fission and Fusion
Nuclear energy derives from atomic nuclei through two distinct processes. Nuclear fission splits heavy unstable nuclei like uranium-235 into lighter elements, releasing approximately 200 MeV per fission event. This process creates a self-sustaining chain reaction when neutrons produced during fission trigger additional splits, controlled in nuclear reactors for power generation. One kilogram of uranium-235 yields energy equivalent to 2,500 tons of coal.
Nuclear fusion combines light nuclei to form heavier elements, releasing even greater energy per unit mass than fission. While fusion powers the sun through hydrogen-to-helium conversion, terrestrial fusion reactors remain experimental due to the extreme temperatures and pressures required to overcome electrostatic repulsion between positively charged nuclei.
Key Energy Formulas Reference Table
| Formula Name | Mathematical Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Energy-Mass Equivalence | E = mc² | Relates mass defect to energy release in nuclear reactions |
| Kinetic Energy | KE = ½mv² | Energy possessed by moving objects (wind, water) |
| Power Generation | P = Energy/Time | Rate of energy conversion in power plants |
| Solar Cell Efficiency | η = (Pout/Pin) × 100% | Percentage of solar energy converted to electricity |
| Energy from Fission | E = Δm × 931 MeV/amu | Energy released per atomic mass unit lost |
| Thermal Efficiency | η = (Wout/Qin) × 100% | Efficiency of heat engine conversion |
| Wave Energy | E = ½ρgH²L | Energy per unit length of ocean wave |
| Wind Power | P = ½ρAv³ | Power available from wind turbine |
Balancing Energy Needs with Sustainability
The transition from conventional to renewable energy sources represents a critical challenge for sustainable development. While fossil fuels currently provide reliable, energy-dense power, their environmental impact and finite nature demand investment in renewable alternatives. Solar, wind, and ocean technologies offer pollution-free energy but require technological advancement to match fossil fuel efficiency and reliability. Nuclear energy provides immense power potential but raises safety and waste management concerns. The optimal energy strategy combines multiple sources, leveraging each technology's strengths while minimizing environmental impact and ensuring long-term energy security for future generations.
Energy is the capacity of a body for doing work. Energy stored in a body or a system is equivalent to total work done by the body till whole of its energy has been completely exhausted. Most of our energy requirement is fulfilled from the fuels & electricity. Solar energy is also available to us in the form of a variety of fuels that have been stored in the earth's crust. Energy can be converted from one form to another.
What is a good source of energy?
Energy is the ability or capacity to do work and in our daily lives we use energy from various sources for doing work. We use electricity to light our street lamps, diesel to run the trains, energy in our muscles help to cycle to school, etc.
The muscular energy for carrying out physical work, electrical energy for cooking food or running a vehicle all come from some source. Thus,
A Source of energy is that which is capable of providing enough useful energy at a steady rate over a long period of time.
We need to know how we select the source needed for obtaining the energy in its useable form. For example, while selecting a fuel, we should keep in mind the following criteria:
- How much heat does it release on burning?
- Does it produce a lot of smoke?
- Is it easily available?
Apart from providing abundant useful energy, a good source of energy should be:
- Safe and convenient to use,
- Do large amount of work per unit volume or mass,
- Easy to store and transport,
- Most importantly, economical.
Classification of source of energy
The sources of energy are classified as follows :
Renewable sources of energy (or non-conventional sources of energy):
The sources of energy which are in constant supply to us by nature and are inexhaustible are known as renewable sources of energy.
e.g. the sun (solar energy), oceans, tidal energy, wind energy, running water energy, wood, geothermal energy etc.
Non-renewable sources of energy (or conventional sources of energy) :
The sources which can't be used again and again and are exhaustible are known as non-renewable sources of energy.
e.g. coal, natural gas, petroleum; fossil fuels etc.
Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy:
They can be studied as follows:
Conventional sources of energy
These are used extensively and meet a major portion of our energy requirement since ancient times.
Examples of conventional sources of energy are fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), hydro energy, biomass (firewood, animal dung and biodegradable waste) energy, wind energy, etc.
Non-conventional sources of energy:
These sources of energy are not used as extensively as the conventional ones and meet our energy requirement only on limited scale.
Examples of non-conventional sources of energy are solar energy, ocean energy (tidal energy, wave energy, ocean thermal energy, etc), nuclear energy, etc.

Conventional Sources of Energy
The various types of conventional sources of energy are as follows:
Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are the remains of the prehistoric animals or plants, burried under the earth, millions of years ago.
e.g. coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Fossil fuels are formed in the absence of oxygen. The chemical effects of pressure, heat and bacteria convert the burried remains of plants & animals into fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas.
It was the sunlight of long ago that made plants grow, which were then converted into fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are energy rich compounds of carbon, which were originally made by the plants with the help ot sun's energy.
Types of fossil fuels
The various types of fossil fuels are:
Coal
It is the most abundant fossil fuel on the earth which is essentially carbon. It is used as a combustion fuel. The exploitation of coal as a source of energy made the industrial revolution possible. Increasing industrialization has led to a better quality of life all over the world. Coal is the principal source of heat for electricity generation and is used as a reducing agent (coke) in heavy industries like iron and steel.
Petroleum
Petroleum (also called crude oil) is a thick black liquid and is not used as fuel in its natural form. It is refined by the process of fractional distillation to obtain a number of useful components like fuel oil, kerosene, diesel oil, petrol or gasoline and petroleum gas. On liquefaction, petroleum gas changes into a liquid which is called liquefied petroleum gas (lpg). It is used for cooking.
Efficiency and use of fossil fuels:
The pollution caused by burning fossil fuels can be reduced by increasing the efficiency of the combustion process and using various techniques to reduce the escape of harmful gases and ashes into the surroundings. Besides being used directly for various combustion process, fossil fuels are the major fuels used for generating electricity, a form of energy which has become a necessity in today’s scenario.
Thermal Power Plant
A “thermal” power plant as the name suggests generates electric power from large amount of heat produced by burning fossil fuels, I.E., coal and petroleum. Fossil fuels are burnt in large amounts in power stations to heat up water to produce steam which further runs the turbine to generate electricity. Transmission of electricity is more efficient than transporting coal or petroleum over the same distance. Therefore, many thermal power plants are set up near coal or oil fields.

Hydro (hydel) Energy
Solar energy appears in the form of energy of water flowing in the rivers which is obvious from the water cycle in nature.
Hydro Electric Power Plant
Hydro electricity is the electricity produced from the kinetic energy of flowing water and a plant which generates hydroelectricity on a large scale is called hydro electric power plant.
A quarter of our energy requirement in india is met by hydropower plants. Since there are very few waterfalls which could be used as a source of potential energy, hydro power plants are mostly associated with dams.
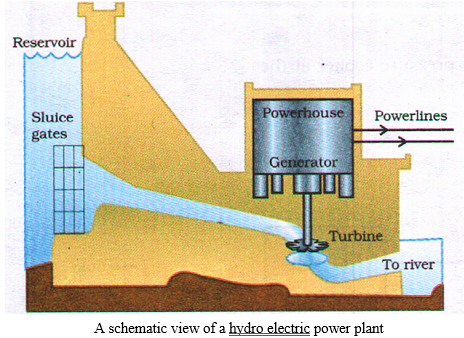
Steps for generation of hydro electricity
The various steps for generation of hydro electricity are :
- Water is collected in storage dams (high rise structure) where kinetic energy of flowing water is transformed into its potential energy.
- Water from the dam is allowed to fall through pipelines over the blades of a turbine at the bottom of the dam. The potential energy of water changes into its kinetic energy which is transferred to the turbine.
- Moving turbine changes the kinetic energy of water into electricity.
Advantage of hydel power:
- The process of hydel power does not cause any environment pollution.
- The moving water needed for the purpose is available free of cost.
- Water energy is a renewable source of electrical energy which will never get exhausted.
- The construction of dams on rivers helps in controlling floods and in irrigation.
Limitations of hydel power
Moving or flowing water is not available at all places. It is available near the sites of flowing rivers.
To generate a reasonable amount of electricity from water, fast moving water should be available in large quantities.
The construction of dam on a river disturbs the ecological balance in downstream area of the river.
The soil in the downstream area may become poor in quality because there were no annual floods to deposit nutrient rich silt on the bank of the river. Therefore there may be ecological problems.
Improvement in the technology for using conventional sources of energy
Biomass and Bio Energy
If we can ensure that enough trees are planted, a continuous supply of fire-wood can be assured. Even the cow-dung cake serves as a fuel. These fuels called biomass are plant and animal products.
Biomass as a Fuel
Biomass is an important source of energy (bio-energy). There are many ways in which biomass can be used as a fuel. However traditional use of these biomass has many disadvantages.
- Traditional use of biomass
The use is: The simplest way of using biomass is to allow it to dry out in the sun and burn it.
- Disadvantages of traditional use of biomass
- The calorific value of these fuels is low.
- They produce a lot of smoke and some harmful gases when they are burnt.
Improvement in technology
This has resulted in using the conventional sources of energy more efficiently such as:
- Fermentation of biomass produces ethanol which is a potential substitute for petrol and diesel.
- Charcoal formation where wood is burnt in unlimited supply of oxygen, water and volatile materials present in it get removed. Charcoal burns without flames, is comparatively smokeless and has higher heat generation efficiency.
- Coke is produced when coal is subjected to destructive distillation (I.E., heating strongly in the absence of air), which is a better fuel than coal as it does not produce smoke on burning.
- Anaerobic digestion of biomass produces biogas.
Biogas
The decomposition which takes place in the absence of oxygen is called anaerobic degradation. Anaerobic degradation is carried out by anaerobic bacteria. Biogas is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide. The major constituents of biogas is methane. Biogas is produced by the anaerobic degradation of animal wastes like animal dung in the presence of water.
Biogas plant
Biogas is prepared by anaerobic degradation of animal wastes like cow dung in biogas plant. The two types of biogas plant are :
- Floating gas holder type biogas plant.
- Fixed-dome type bio-gas plant.
The raw material used for producing biogas in both the plants is the same, it is a mixture of cattle dung and water.
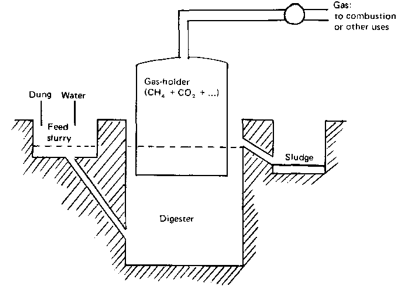
Floating gas holder type bio-gas plant
This biogas plant consist of a well shaped underground tank called digester, which is made up of bricks. A drum shaped gas holder made of steel floats in the inverted position over the dung slurry in the digester tank. Since the gas holder floats over the dung-slurry, so this biogas plant is called floating gas-holder type biogas plant. The gas holder can move up and down, and its movement is controlled by the control pipe. There is a gas outlet at the top of the gas holder tank having a valve.
A partition wall divides the digester tank in two parts: on the left of the digester tank is an inlet pipe made of cement (the inlet is connected to a mixing tank, on the right side of the digester tank is an outlet pipe, also made of cement, which is connected to an over-flowtank. The inlet pipe is for feeding the fresh dung slurry into the digester tank whereas the outlet pipe is for removing the spent dung after the extraction of biogas. Cattle dung and water are mixed in equal proportions in the mixing tank to prepare the slurry.
This slurry of dung and water is fed into the digester tank through the inlet pipe. The dung undergoes anaerobic degradation in the presence of water with the gradual evolution of biogas. As more and more bio-gas collects in the gas-holder, the pressure of gas in it increases. As the spent dung slurry goes out, more fresh dung slurry is added to the digester tank on daily basis.
Fixed dome type biogas plant
This biogas plant is a dome-like structure built with bricks and consists of the following parts:
- Mixing tank: it is a tank where the slurry (semi fluid mixture) of animal dung and other waste materials is prepared by mixing it with an equal amount of water.
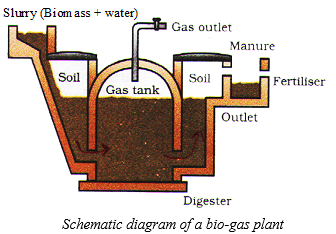
- Digester tank: the slurry so prepared is fed into the digester tank through an inlet chamber. The digester is a sealed chamber with no oxygen. The anaerobic microbes decompose complex compounds of the slurry within few days (50-60 days) and produce biogas.
- The biogas keeps collecting in the dome. It exerts pressure on the slurry in the digester tank which forces the spent slurry into the overflow tank through an outlet chamber.
- To get a continuous supply of biogas, fresh slurry is periodically added to replace the spent slurry.
Composition and Advantages of Biogas
Biogas in mainly composed of methane (upto 75%), co2 (25%) and traces of other gases such as nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide and hydrogen. The advantages are as follows:
- Biogas is a clean fuel that burns without smoke and leaves no ash like in wood, charcoal and coal burning.
- The main constituent of biogas, I.E., methane has a higher calorific value than that of petrol.
- The spent slurry being rich in nitrogen and phosphorus is good manure.
- By using biogas, firewood is saved and deforestation is reduced.
- The large-scale utilization of bio-waste and sewage material provides a safe and efficient method of waste-disposal besides supplying energy and manure.
Wind energy
Moving air is called wind. As the moving objects possess k.E. And as such they are capable of doing mechanical work by virtue of its motion. Wind also possess the ability of performing mechanical work because it is air in motion. So wind energy is the k.E. Associated with large mass of air by virtue of its motion.
Solar energy is responsible for the blowing of air.
This can be explained as follows: the sunrays fall on the earth but the intensity of sun-rays is much stronger near the equator than in the polar regions. Due to more intense sun-light, the air near the surface of earth in equitorial regions becomes quite hot. This hot air, being lighter, rises upwards. The cooler air from the polar regions of the earth start flowing towards the equitorial regions of the earth to fill the space vacant by the hot rising air. In this way air flows from the higher pressure regions to the lower pressure regions of the earth. This flow of air from one place to another constitutes wind.

Advantages of wind energy
- Use of wind energy does not lead to pollution.
- Wind energy is available free of cost.
- The source of wind energy I.E. Air is an inexhaustible and reversible source.
Disadvantages of wind energy
- One of the most important limitation of wind energy is that it may not be available at all times.
- The windmill and sail-boats remain un-operational and no useful work can be done unless there is a plenty of fast blowing wind.
- The speed of the wind at a place varies with time and season.
- The k.E. Of the wind can be utilized only at the site.
- There is no guarantee that we will get wind energy when required, since there is no place in the world where wind blows all the time.
- The wind is not predictable.
Wind Mill
A windmill is a machine, which works with the energy of blowing air or wind. It consists of large blades to catch the wind. When the wind strikes against these blades, they start rotating. The motion can then be passed on the other connected parts & is used to do useful work. A windmill consists of a system of big blades (or vanes) capable of rotating about a horizontal axis. The system of vanes is mounted on the top of a high tower. Its working is based on the tansformation of k.E. Of wind into the rotational energy of the blade. The system of blades is connected to one end of the rod called shaft. The other end of the shaft is connected to a pump rod in case of water pump. This end is bent in form of inverted v and is connected to the free end of the pump rod of the water pump. When the wind blows, it rotates the blades of the windmill. The shaft turring about its axis rotates the crank. The rotation of the crank moves the piston rod of the water pump up and down & draws water from the well.
Windmill to operate flourmill
It is similar to one used to grind grains by suitable arrangements of toothed wheel & shafts. The other end of the shaft is connected to a toothed wheel. Grinding arrangement of flour mill has a fixed mill stone a and another heavy mill stone b. B is capable of rotating by a shaft rod (w2) having a toothed wheel (w2). The wheel (w1) is coupled with the wheel (w2) such that the rotation of wheel (w1) about a horizontal axis rotates the wheel (w2) about a vertical axis. The wheel (w1) rotates as the shaft (w1) connected to blades rotates due to rotation of blades of windmill. Thus the k.E. Of wind by virtue of this motion rotates the windmill which in turn operates a flourmill and is able to grind grains.
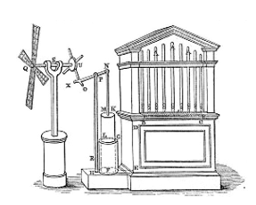
Wind generator
A modern generator, which is used to generate electricity by using wind energy is wind generator. When the fast moving wind strikes the blades of wind turbine, then the wind turbine starts rotating continuously. The coil of a small electric generator is attached to the shaft of wind turbine. So when the wind starts rotating and generates electricity. The electricity generated by a single wind turbine is quite small. So, in order to generate a large amount of electricity, a large amount of wind turbines are placed over a big area of land. Such a set-up of having a large number of wind turbines working at a place to generate electrical energy on a large scale is called a wind energy farm.
Alternative or non-conventional sources of energy
Our demand for energy is increasing day by day as our life-styles are also changing. As our demand for energy increases, we need to look for more and more sources of energy. So technologies are developed to use the available or known sources of energy more efficiently and also look to new sources of energy.
Solar energy
The sun is the primary source of energy for all living beings on the earth. It provides all of us heat and light. The energy generated by the sun is the result of reaction called nuclear fusion, occurring continuously in the interior part of the sun. Hans bethe, a physicist proposed that the enormous release of energy from the sun is due to the fusion (combination) of four hydrogen atoms to yield a single helium atom ( he).
For this discovery he was awarded the 1967 noble prize in physics. The sun emits energy in all directions in space.
Solar energy is trapped by plains, plateaus, mountains, rivers, lakes, oceans and ponds. Plants use solar energy to manufacture food by photosynthesis and also solar energy is the source of wind storms, rain, snowfall & ocean waves.
It is the perennial (forever) source of energy.
This perennial source of energy has some features:
- It comes to earth surface in a very diffused form.
- Upper atmosphere gets 1.3 kj of energy per second per square meter of this only 47% I.E. Approximately 0.64 kj energy reaches per second per square meter on earth's surface.
- Mreover this amount of energy is not available uniformly and keeps changing everyday at a place and place to place during a day.
Composition of solar energy (sunlight)
Ultra violet rays
The invisible rays whose wavelength is shorter than that of the visible violet light are called ultra violet rays. We can detect these rays by using a photographic film or a fluorescent paper because they darken the photographic film just like ordinary light rays. They are used to kill bacteria in food and drinking water. Too much ultra-violet radiation is dangerous for our health due to its ionising effect and can cause skin cancer.
Visible light
The visible rays whose wavelength range from 400 nm (in violet) to 700 nm (in red) are called visible light the visible part of the sunlight consists of seven dififerent wavelength, each wavelength corresponding to a different colour. Thus the visible part of the sunlight consists of seven different colours.
Infra-red rays
The invisible rays whose wavelength is longer than that of the visible red light are called infra-red rays. They can heat the object on which they fall. About one-third of the solar energy consists of infra-red rays. They can be detected by its heating effect, by using a thermometer. Every hot object emit infra-red rays. They are used to get relief frorn bodyaches.
Uses of solar energy
- Solar cooker absorb solar energy and cook food.
- Solar water heaters are used for heating water.
- Solar cell convert solar energy into electricity to run watches, calculators and in spaceships for various experiments.
- Solar energy is absorbed by green plants to make their food by photosynthesis.
- Solar energy is used for drying clothes and food grains.
- Solar energy is used for making salt from sea water.
Advantages of solar energy
- It is inexhaustible and renewable as it is being produced continuously in the core of sun by nuclear fusion of h-atoms.
- Its quantity is unlimited and is available in all parts of the world in abundance.
- It does not cause any pollution.
- It can be put to practical applications.
Limitations of solar energy
- It is not available at night.
- It is not available uniformly in all parts of world.
- Solar energy received by the earth is quite diffused and in scattered form and hence only a part of it is utilized.
- It is not available at constant rate due to clouds, fog, mist, haze, winds etc.
Direct and indirect harnessing (or collection) of solar energy
- Direct utilization of solar energy can be done by collecting the heat radiated on reflecting these by plane mirrors on to black boxes containing uncooked food (in solar cooker) and for heating water in solar heaters. These rays can be converted into electrical energy as in solar cells.
- Indirect utilization of solar energy can be done by first converting solar energy into chemical energy as in biomass of plants. Heat energy of sun can be utilized in sea waves (ocean thermal energy) and into energy of winds etc.
Solar heating devices
These are the devices which can collect and store heat obtained from solar energy.These are used for heating and cooking purposes. Solar heating devices are designed in such a way so that these can make maximum utilization of solar heat radiations. It is done by adopting following procedure:
- Concentration of solar energy by using reflectors: for moderate heating sun rays are reflected by using plane mirrors, as in solar cookers and solar water heaters. For high temperature, sun's energy is concentrated using concave mirrors as reflectors.
- Black paint : since black bodies are good absorbers as well as good radiators of heat, hence black paint is used to absorb and store heat radiations in large quantity by using large surface area.
- Glass-sheet cover: glass sheet cover is used to protect the hot infrared rays of solar energy from escaping the body of black box. It allow the ir radiations (of shorter wavelength) to enter the box of solar heating device and do not allow ir radiations (of longer wavelength) to escape from the solar heating device. Hence, more heat is retained by solar heating device for long time.
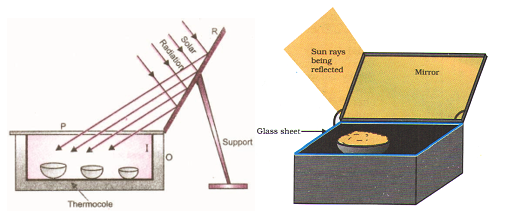
Box type solar cooker
A solar cooker is a device which is used to cook food by utilizing the heat radiation coming from the sun. There are two types of solar cookers:
A box type solar cooker is based on the following facts:
Principle
A box –type solar cooker is based on the principle of green house effect. Glass reflects infrared radiations of longer wavelengths but allows those with shorter wavelengths to pass through. The solar radiation which passes through the glass heats up the surfaces inside the the box. These warm surfaces then radiate heat. This radiation consists mainly of ir of longer wavelengths. They are reflected by the glass. This process of heating is called greenhouse effect.
Construction
- Outer wooden box (o) with thermo cole lining – it prevents the loss of heat generated by green house effect from the box.
- Inner black painted metal box (I) – a black body is a good absorber of the heat radiation. The blackened surface absorbs maximum amount of heat (98%) and prevents heat loss due to reflection.
- Reflector (plane mirror), r – it increases the effective area for the collection of solar energy.
- Gass cover plate (p) – the purpose of glass cover plate is to trap heat radiations. It transmits 50% of heat radiation when it is coming from a source like the sun which is at a high temperature. But, when the radiations come from a source which is at a lower temperature, glass is opaque to them I.E., it does not allow the radiations to pass through it. Thus, the glass cover placed on the box produces a kind of green house effect.
Working:
The sun light falls on the plane mirror (reflector) which concentrates the light to the glass cover plate. The cover plate (p) heats up the metal box by green house effect. This heat is conserved by the black paint and outer wooden box (o).
Uses:
The temperature inside the cooker can go upto 100°c – 140°c when kept in the sun for two to three hours. These cookers are provided with small containers so that 2 – 3 items can be cooked simultaneously.
Merits and demerits of solar cookers
The various merits and demerits of solar cookers are as follows:
Merits
- Solar cookers do not require fuel and hence cause no pollution.
- The nutritional value of the food remains intact.
- Maintenance cost is low.
Demerits
- Food cannot be cooked at night or during cloudy days.
- Cooking takes more time.
Spherical reflector type solar cooker
In this type of solar cooker, there is an insulated metal box, painted black from inside. A spherical reflector is used here (in place of plane mirror) because a very high temperature is required, the spherical reflector is either a concave reflector or a parabolic reflector. The sunlight falling on the surface of spherical reflector get concentrated at one point. This produces a lot of heat at that point & temperature of that region becomes very high, therefore a utensil is placed at that point. Since a high temperature can be produced, so it can be used for making chappaties and for frying purposes.

Difference between box - type & spherical reflector type solar
| Box Type Solar Cooker | Spherical Reflector type Solar Cooker | ||
| 1. | a plane mirror reflector is used. | 1. | spherical reflector is used |
| 2. | in a box type solar cooker, comparatively low temperature is produced | 2. | quite high temperature is produced in the spherical reflector type solar cooker. |
| 3. | it cannot be used for making chappaties | 3. | it can be used for frying and making chappaties. |
| 4. | used for cooking food requiring slow heating | 4. | used for cooking food requiring strong heating |
Solar cell
Thus, the limitations of using solar energy is overcome by using solar cells. It was in the year 1954 when the first practical solar cell, which could convert about 1% of the solar energy into electric energy, was fabricated. A typical solar cell consists of a 2 cm square piece of almost pure silicon can develop a voltage of 0.5v – 1v and can produce about 0.7 w of electricity when exposed to the sun.
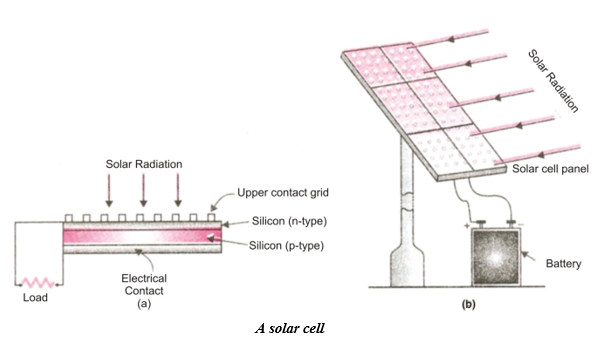
Semi-conductors
Semi-conductors are those substances which have very low electrical conduciivity. Under ordinary conditions, semi-conductor materials conduct only a small amount of electric current. But if certain impurities are added to semi-conductor materials then their electrical conductivity increases considerably. Semi-conductors are neither good conductor of electricity nor they are completely insulators. The process of adding impurity is called doping. The material (semiconductors) doped with boron has an affinity to attract electrons and is termed as p-type (acceptor) semiconductor. The phosphorous doped silicon material, which has a surplus of electrons, is termed as n-type (donor) semiconductor. When solar energy fails on semi-conductor material, even then their electrical conductivity increases.
Conduction of solar cell
It is constructed usually from silicon & gallium. Its conductivity increases when light falls on it. Therefore in a solar cell, the pieces (usually wafers) of semi conducting materials containing impurities are so arranged that when light falls on them then a potential difference is produced between two regions of the semi conductor. It has been observed that a solar cell of about 4 cm2 may produce potential difference of about 0.4v to 0.5v and generate a current of 60 ma. A large number of solar cells joined together in a definite pattern can provide much higher power for many use. The group of solar cells is called solar cell panel.
Solar cell panel
When solar cells are arranged side by side, connecting each other in such a way that total potential difference and the total capacity to provide electric current is increased to a large extent the arrangement is called solar cell panel. The electric power required for the working of artificial satellites in outer space, street lighting in remote areas and running of irrigation water pumps in far-off areas obtained with the help of solar cell panels. In a solar cell panel hundreds of solar cells are joined together, the electricity produced by this solar panel is stored in battery. This battery runs an electric motor and finally the motor drives the water pump, which pumps out the underground water. The various solar cells in a solar cell panel are joined together by using connecting wires made of silver. This is because silver metal is the best conductor of electricity having very low resistance. The use of silver for connecting solar cells makes the solar cell panel more expensive but it increases the efficiency. This is because if connecting wires of other metals were used in solar cell panel, then a substantial part of the electricity generated by it could be lost in overcoming the resistance of such connecting wires.

Advantages of solar cells/ solar cell panels
They have no moving parts, require little maintenance and work quite satisfactorily without the use of any focusing device.
They can be set up in remote and inaccessible areas in which lying of power transmission line may be expensive and not commercially viable.
Silicon which is used in solar cells is available abundantly and is also ecofriendly.
Disadvantages
Special grade silicon for making solar cells is limited.
The entire process of manufacture is still very expensive. Silver used for interconnection of the cells in the panel further adds to the cost.
Uses of solar cell
Solar cells are used for providing electricity in artificial satellite and space probes.
In india, solar cells are being used for street lighting, for traffic signals, for operating water pumps and for running radio and television sets in remote areas.
Solar cells are used for providing electricity to "Lighthouses" situated in the sea and to the off-shore oil drilling rig platforms.
Solar cells are used for operating electronic watches & calculators.
Energy from the sea
Oceans are large water bodies which covers about 70.8% of the earth’s total surface area. They are the huge reservoirs of energy which can be obtained for useful purposes in a variety of ways. Following are the most common ways of obtaining the energy from the oceans:
Tidal energy
Tides are everyday movement of water level along the coasts. Tides are due to the gravitational pull of the moon on the spinning earth. This pull varies during the monthly cycle of rotation of the moon around the earth. The level of water may rise upto a few metres in high tides which occur on every new moon day and full moon day.
The energy derived from rising and falling ocean tides is called tidal energy. Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing a dam. A turbine fixed at the opening of the dam converts tidal energy to electricity. However, energy generation requires:

Merits
- It is an inexhaustible and renewable pollution-free source of energy.
- It is independent of uncertainty of rainfall.
Demerits
- Power generation is intermittent due to variation in tidal range.
- The most difficult problem in the use of tidal power is the barrage construction in areas of high tidal flow and corrosion of barrage.
Wave energy
Due to the blowing of wind on the surface of ocean, very fast sea-waves move on its surface. Due to their high speed, sea waves have a lot of kinetic energy in them. The energy of moving sea-waves can be used to generate electricity. This can be done as follows :
- One idea is to set up floating generators in the sea. These would move up and down with the seawaves. This movement would drive the generators to produce electricity.
- Another idea is to let the sea-waves move up and down inside large tubes. As the waves move up, the air in the tubes is compressed. This compressed air can then be used to turn a turbine of a generator to produced electricity.

Merits of wave energy
- It is a renewable and pollution free source of energy.
- It does not require large land areas.
Demerits of wave energy
- The power supply is variable in nature due to variability in wave formation.
- Marine life could be affected due to wave energy harnessing structures.
Ocean thermal energy:
The energy available due to the difference in the temperature of water at the surface of the ocean and at a deeper levels is called ocean thermal energy. the drives used to harness ocean thermal energy are called ocean thermal energy conversion power plants. A temperature difference of 20°c between the surface water of ocean and deeper water is needed for operating otec power plants. In one type of otec power plant, the warm surface water of ocean is used to boil a liquid like ammonia or a chlorofluorocarbon (cfc). The high-pressure vapours of the liquid are then used to run the turbine of a generator and produce electricity. The colder water from the deeper ocean is pumped up to cool the used up vapours & convert them again into a liquid. This process is repeated again and again.
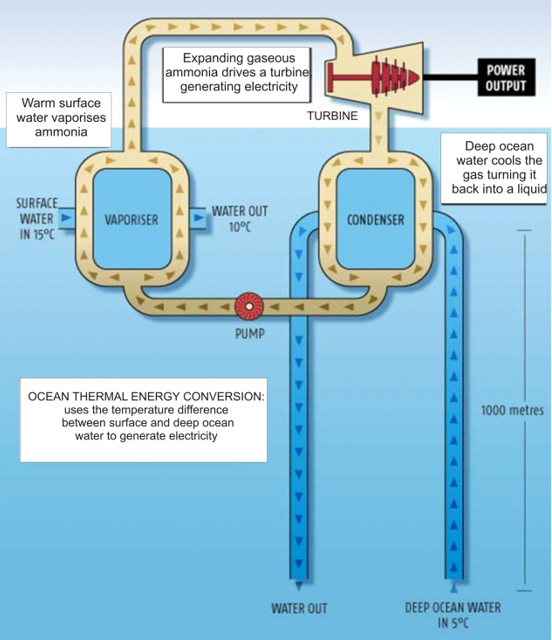
Otec power plants
These plants can operate if the temperature differences between the water at the surface and water at depths upto 2 km is 293 k (20°c) or more. The plant undergoes the following cycle of operations.
- The warm surface water is used to vapourize pressurized ammonia (approx. 8 atm) in an evaporator (I.E., a heat exchanger) through which warm sea water flows.
- The vapours are then used to turn a turbine of generator to generate electricity.
- The cold ocean water is transported to the surface and is used to condense ammonia vapour through a condenser.
- The ammonia condensate (condensed ammonia vapour) is pumped back to the evaporator through a pump.
Merits of otec
- The electric power produced is continuous, renewable and pollution free.
- Otec system does not have daily or seasonal variations in their output as in case with the solar energy devices.
Demerits of otec
- Otec system requires a lot of capital investment.
- The conversion efficiency is low as there is small temperature difference between the surface water and the deep water.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the heat energy of hot rocks present inside the earth. This heat can be used as the source of energy to produce electricity. Geothermal energy is one of the few sources of energy that do not come directly or indirectly from solar energy. The places where very hot rocks occur at same depth below the surface of earth are called ‘hot spots’ and are sources of geothermal energy.
The geothermal energy is harnessed as follows:
- The extremely hot rocks present below the surface of earth, heat the underground water and turn it into steam. As more and more steam is formed between the rocks, it gets compressed to high pressures. A hole is drilled into the earth and the hot rocks comes up through the pipe at high pressure. This high-pressure steam run the turbine of a generator to produce electricity.
- Large rocks are present in the underground rocks, which allow steam and hot water to go up. The steam & hot water gushing out of the ground are a kind of natural geyser. This steam is then used to turn turbines and generate electricity and the hot water is used to cook food.

Merits of geothermal energy
- It is the most versatile and least polluting renewable source of energy.
- It is relatively inexpensive and power generation level is higher as compared to solar energy and wind energy.
Demerits of geothermal energy
- Though geothermal energy is inexhaustible, a single bore has a limited life span of about 10 years.
- Geothermal hot spots are scattered.
Environmental consequences of exploiting sources of energy
Environment is disturbed whenever a source of energy is used to derive energy from it.
- Burning of fossil fuels cause air-pollution.
- Construction of dams destroys large ecosystems and creates problem of rehabilitation of displaced population.
- Continuous whirling and whistling of windmills cause noise-pollution and plays havoc with the lives of migratory birds.
- Heavy energy structures to exploit wave energy affect marine mammal and seabird population.
- Using wood as fuel results in deforestation which affects environment.
How long will an energy source last us?
- Fossil fuels (coal, petroleum and natural gas) will get depleted some day as these are exhaustible sources of energy. It has been estimated that coal will last for another 200 years whereas known reservoirs of petroleum for another 60 years and those of natural gas for about 40 years.
- We can get a continuous supply of biomass only if we plant trees in a planned manner. In case, it is not done so, we would fall short of biomass.
- Geothermal energy is an inexhaustible source of energy.
- Nuclear energy is also inexhaustible as only a small mass of uranium produces large amount of energy, e.G., one atom of uranium produces 10 million times the energy produced by the combustion of an atom of carbon from coal.
- Solar energy, water energy, wind energy and ocean energy are inexhaustible sources of energy.
Solved Examples
Ques. If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Sol. we would use a microwave oven for heating the food as it heats it uniformly and cleanly without loss in its nutritional value.
Ques. How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Sol. the traditional use of wind energy has been modified by using windmills and that of water by constructing hydroelectric power plants.
Ques. What are the two main categories of sources of energy?
Sol.
- Renewable sources of energy
- Non-renewable sources of energy
Ques. How is biogas produced?
Sol. biogas is produced by anaerobic degradation of biomass in the presence of water but in the absence of oxygen.
Ques. What is geothermal energy?
Sol. geothermal energy is the heat of the naturally occurring thermal energy found within rock formations and the fluids held within those formations. It is one of those few sources of energy that do not come directly or indirectly from the solar energy.
Ques. Can any source of energy be pollution-fee? Why or why not?
Sol. no source of energy is totally pollution free-only the degree and the manner of pollution varies. A source of energy like a solar cell is pollution free in actual operation but its assembly causes damage to environment.
Ques. What does a windmill do?
Sol. it converts the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical or electrical energy.
Ques. Name two products obtained during fractional distillation of petroleum which are used as fuel.
Sol. (I) kerosene oil (ii) liquefied petroleum gas (lpg).
Ques. Name the constituent which is found in natural gas as well as in biogas.
Sol. methane.
Ques. Hydrogen has been used as a rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than cng? Why or why not?
Sol. Hydrogen is a cleaner fuel than cng. This is due to the reason that it produces water on burning whereas cng on burning produces co2, though much less than that produced when coal or oil is burnt. A spaceship carries oxygen (in liquid form) along with it to burn hydrogen (in liquid form) as a fuel.
Ques. What kind of mirror-concave, convex or plane-would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Sol. A concave mirror is best suited for use in a solar cooker. This is due to the reason that a concave mirror reflects and concentrates solar energy from over a large area into a small area. Such a mirror is called as solar concentrator.
Ques. Write the disadvantage of traditional use of bio- mass?
Sol. (a) The calorific value of these fuels is low.
(b) They produce a lot of smoke and some harmful gases when they are burnt.
Ques. Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Sol. (I) coal (ii) petroleum and natural gas.
These resources are present only in limited amounts and will be exhausted soon, if we continue to use them at the present rate. These sources were formed over millions of years under special conditions.
Ques. What is good source of energy?
Sol. A good source of energy is one which:
- Performs a large amount of work per unit volume or mass,
- Is easily accessible,
- Is easy to store and transport,
- Is economical.
Ques. What is a good fuel?
Sol. A good fuel is one which:
- Has high calorific value, I.E., produces large amount of heat on burning completely in air or oxygen,
- Produces less smoke on burning,
- Has low cost and is easily available,
- Has an ignition temperature that is well above the normal temperature.
Ques. Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Sol. Fossils fuels were formed due to extraordinary conditions that prevailed on the earth many million years ago. No new reservoirs of these fuels are being formed due to the absence of these conditions. As such fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy. In case we continue to use these sources at the present rate, we would soon be deprived of these sources. It is due to this reason that we should conserve these sources and look for alternate sources of energy.
Ques. On what basis would you classify energy sources as:
(a) Renewable and non-renewable?
(b) Exhaustible and inexhaustible?
Are the options given in (a) and (b) the same?
Sol. (a) Renewable sources of energy are those (I) which can be replaced as we use them and (ii) which can be used to produce energy again and again.
Non-renewable sources of energy are those which cannot be replaced once these are used.
(b) Exhaustible sources of energy are those whose supply is limited, e.G., coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Inexhaustible sources of energy are those whose energy supply is unlimited, e.G., solar energy, water energy, wind energy, nuclear energy, etc.
Renewable sources of energy are inexhaustible whereas non-renewable sources of energy are exhaustible with some exceptions. For example, biomass is a renewable source of energy only if we plant trees in a planned manner. On the other hand, geothermal energy and nuclear energy though inexhaustible are non-renewable.
Ques. What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption?
Sol.
- Burning of fossil fuels to meet increasing demand for energy causes air-pollution.
- Construction of dams on rivers to generate hydroelectricity destroys large ecosystems which get submerged under water in the dams. Further, large amount of methane (which is a greenhouse gas) is produced when submerged vegetation rots under anaerobic conditions.
- Continuous whirling and whistling of windmills cause noise-pollution and plays havoc with the lives of migratory birds.
- Heavy energy structures to exploit wave energy affect marine mammal and seabird population.
- Using wood as fuel results in deforestation which affects environment.
In order to reduce energy consumption:
- Fossil fuels should be used with care and caution to derive maximum benefit out of them.
- Fuel saving devices such as pressure cookers etc. Should be used.
- Efficiency of energy sources should be maintained by getting them regularly serviced.
- Last of all, we should be economical in our energy consumption as energy saved is energy produced.