Chapter-9. Mineral and Power Resources
“Mineral and Power Resources” teaches students about different minerals, their uses, and distribution across the world. It also covers renewable and non-renewable energy sources and the importance of conservation.
To ensure concept clarity, the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 guide students through important definitions and examples. Class 8 Notes offer a quick summary of metallic and non-metallic minerals, energy production, and global reserves. Class 8 Home Tuition sessions make learning interactive with real-world case studies and current examples. This chapter deepens students’ knowledge of how resources shape economies and how energy choices affect the planet’s future.

What are Minerals?
A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is a mineral. Minerals are one of the most important resources of a country. They are of different types and provide sound base for eoonornic and industrial development. Minerals are not found equally distributed over space. They are concentrated in a particular area or rock formations. Minerals are formed in different types of geological environments, under varying conditions. They are created by natural processes without any human interference.
.png)
Types Of Minerals:
Minerals are classified on the basis of physical properties, such as colour density, hardness and chemical properties such as solubility.
On the basis of composition, minerals are classified mainly as metallic and non-metallic minerals. The metallic minerals contain metal in raw form. Metals are hard substances that conduct heat and electricity and have a characteristics lustre or shine. Iron ore, bauxite, manganese ore are some examples. Metallic minerals may be ferrous or non-ferrous.
Ferrous minerals like iron ore, manganese ore and chromite contain iron. A non-ferrous mineral does not contain iron but may contain some other metal such as gold, silver, copper or lead. The non-metallic minerals do not contain metals. Limestone; mica and gypsum are examples of such minerals. The mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are also non-metallic minurals.
- Extraction of Minerals:
The process of taking out minerals from rocks buried under the earth's surface is called mining. Minerals that lie at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer; this is known as open-cast mining.
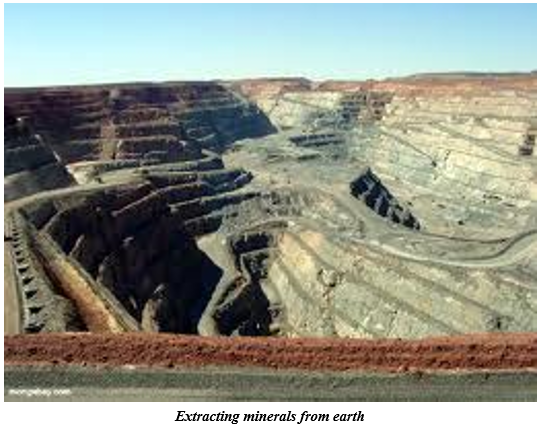

Deep bores, called shafts have to be made to reach mineral deposits that lie at great depths. This is called shaft mining. Petroleum and natural gas occur far below the earth's surface. Deep wells are bored to take them out, this is called drilling. Minerals that lie near the surface are simply dug out by the process known as quarrying.
Distribution of Minerals:
Minerals occur in different types of rocks. Generally, metallic minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rock formations that form large plateaus. Iron-ore in north Sweden, copper and nickel deposits in Ontario, Canada, iron, nickel, chromites and platinum in South Africa are examples of minerals found in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
Sedimentary rock formations of plains and young fold mountains contain non-metallic minerals like limestone. Limestone deposits of Caucasus region of France, manganese deposits of Georgia and Ukraine and phosphate beds of Algeria are some examples. Mineral fuels such as coal and petroleum are also found in the sedimentary strata.
Do Check - How, When and Where
Worldwide Distribution Of Minerals
- Asia:
China and India have large iron ore deposits. The continent produces more than half of the world's tin. China, Malaysia and Indonesia are among the world's leading ten producers. China also leads in production of lead, antimony and tungsten. Asia also has deposits of manganese, bauxite, nickel, zinc and copper.
- Europe
Europe is the leading producer of iron-ore in the world. The countries with large deposits of iron ore are Russia, Ukraine, Sweden and France. Minerals deposits of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel are found in Eastern Europe and European Russia.
- North America:
Iron ore, nickle, gold, uranium and copper are mined in the Canadian Shield Region, coal in the Appalachians region. Western Cordilleras have vast deposits of copper, lead, zinc, gold and silver.

- South America:
Brazil is the largest producer of high grade iron - ore in the world. Chile and Peru are leading producers of copper. Brazil and Bolivia are among the world's largest producers of tin. South America also has large deposits of gold, silver, zinc, chromium manganese, bauxite, mica, platinum, asbestos and diamond. Mineral oil is found in Venezuela, Argentina, Chile, Peru and Columbia.
- Africa:
It is the world's largest producer of diamonds, gold and platinum. South Africa, Zimbabwe and Zaire produce a large portion of the world's gold. The other minerals found in Africa are copper, iron ore, chromium, uranium, cobalt and bauxite. Oil is found in Nigeria, Libya and Angola.
- Australia:
Australia is the largest producer of bauxite in the world. It is a leading producer of gold, diamond, iron ore, tin. and nickel, it is also rich in copper, lead, zinc and manganese. Ka!goorlie and Coolagardie areas of Western Australia have the largest deposits of gold.
- Antarctica
Significant size of deposits of coal in the Transantarctic Mountains and iron near the Prince Charles mountains of East Antarctica is forecasted. Iron ore, gold, silver and oil are also present in commercial quantities.
- Distribution in India:
India is endowed with a rich variety of mineral resources due to its varied geological structure. Bulks of the valuable minerals are products of pre-Paleozoic age and are mainly associated with metamorphic and igneous rocks of the peninsular India. The vast alluvial plain tract of north India is devoid of minerals of economic use.
The mineral resources provide the country with the necessary base for industrial development. A mineral is a natural substance of organic or inorganic origin with definite chemical and physical properties. Minerals may be grouped under two main categories of metallics and non-metallics.
Metallic minerals are the sources of metals. Iron ore, copper, gold produce metal and are included in this category. Metallic minerals are further divided into ferrous and non-ferrous metallic minerals. All those minerals which have iron content are ferrous such as iron ore itself and those which do not have iron content are non-ferrous such as copper, bauxite, etc.
Non-metallic minerals are either organic in origin such as fossil fuels also known as mineral fuels which are derived from the buried animal and plant life such as coal and petroleum. Other types of non-metallic minerals are inorganic in origin such as mica, limestone and graphite, etc.
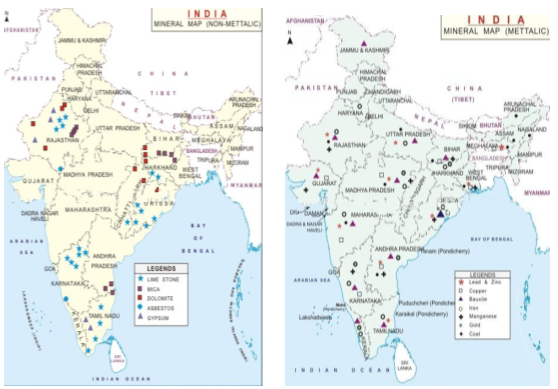
Distribution of Minerals In India:
Most of the metallic minerals in India occur in the peninsular plateau region in the old crystalline rocks. Over 97 per cent of coal reserves occur in the valleys of Damodar, Sone, Mahanadi and Godavari. Petroleum reserves are located in the sedimentary basins of Assam, Gujarat and Mumbai High i.e. off-shore region in the Arabian Sea. New reserves have been located in the Krishna-Godavari and Kaveri basins. Most of the major mineral resources occur to the east of a line linking Mangalore and Kanpur. Minerals are generally concentrated in three broad belts in India. There may be some sporadic occurrences here and there in isolated
pockets.
Do Check - Ruling the Country Side
Mineral Belts of India
- The North-Eastern Plateau Region: This belt covers Chotanagpur (Jharkhand), Orissa Plateau, West Bengal and parts of Chhattisgarh.
- The South-Western Plateau Region: This belt extends over Karnataka, Goa and contiguous Tamil Nadu uplands and Kerala. This belt is rich in ferrous metals and bauxite. It also contains high grade iron ore, manganese and limestone. This belt packs in coal deposits except Neyveli, which has lignite. This belt does not have as diversified mineral deposits as the north-eastern belt. Kerala has deposits of monazite and thorium, bauxite clay. Goa has iron ore deposits.
- The North-Western Region: This belt extends along Aravali in Rajasthan and part of Gujarat and minerals are associated with Dharwar system of rocks. Copper, zinc have been major minerals. Rajasthan is rich in building stones i.e. sandstone, granite, marble. Gypsum and Fuller’s earth deposits are also extensive. Dolomite and limestone provide raw materials for cement industry. Gujarat is known for its petroleum deposits.
- The Himalayan belt: The Himalayan belt is another mineral belt where copper, lead, zinc, cobalt and tungsten are known to occur. They occur on both the eastern and western parts. Assam valley has mineral oil deposits. Besides oil resources are also found in off-shore-areas near Mumbai Coast (Mumbai High).
Spatial Pattern Of Important Mineralsferrous Minerals
Ferrous minerals such as iron ore, manganese, chromite, etc., provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries. Our country is well-placed in respect of ferrous minerals both in reserves and production.
- Iron Ore:
India is endowed with fairly abundant resources of iron ore. It has the largest reserve of iron ore in Asia. The two main types of ore found in our country are haematite and magnetite. It has great demand in international market due to its superior quality.
The iron ore mines occur in close proximity to the coal fields in the north-eastern plateau region of the country which adds to their advantage. The total reserves of iron ore in the country were about 20 billion tonnes in the year 2004- 05. About 95 per cent of total reserves of iron ore is located in the States of Orissa, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Goa, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Manganese:
Manganese is an important raw material for smelting of iron ore and also used for manufacturing Ferro alloys. Manganese deposits are found in almost all geological formations; however, it is mainly associated with Dharwar system.
Orissa is the leading producer of Manganese. Maharashtra is also an important producer of manganese. The manganese belt of Madhya Pradesh extends in a belt in Balaghat-Chhindwara-Nimar-Mandla and Jha ua districts. Andhra Pradesh, Goa, and Jharkhand are other minor producers of manganese.
Do Check - When People Rebel
- Non-Ferrous Minerals:
India is poorly endowed with non-ferrous metallic minerals except bauxite.
- Bauxite:
Bauxite is the ore which is used in manufacturing of aluminum. Bauxite is found mainly in tertiary deposits and is associated with laterite rocks occurring extensively either on the plateau or hill ranges of peninsular India and also in the coastal tracts of the country. Orissa happens to be the largest producer of Bauxite. The pat lands of Jharkhand in Lohardaga have rich deposits. Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra are other major producers.
- Copper:
Copper is an indispensable metal in the electrical industry for making wires, electric motors, transformers and generators. It is alloyable, malleable and ductile. It is also mixed with gold to provide strength to jewellery.
The Copper deposits mainly occur in Singhbhum district in Jharkhand, Balaghat district in Madhya Pradesh and Jhunjhunu and Alwar districts in Rajasthan.
- Non-Metallic Minerals:
Among the non-metallic minerals produced in India, mica is the important one. The other minerals extracted for local consumption are limestone, dolomite and phosphate.
- Mica:
Mica is mainly used in the electrical and electronic industries. It can be split into very thin sheets which are tough and flexible. Mica in India is produced in Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan followed by Tamil Nadu, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh. In Jharkhand high quality mica is obtained in a belt extending over a distance of about 150 km, in length and about 22 km, in width in lower Hazaribagh plateau. In Andhra Pradesh. Nellore district produces the best quality mica. In Rajasthan mica belt extends for about 320 kms from Jaipur to Bhilwara and around Udaipur.
- Energy Resources:
Mineral fuels are essential for generation of power, required by agriculture, industry, transport and other sectors of the economy. They lie in Jharkhand-Bengal coal belt.
- Coal:
Coal is a one of the important minerals which is mainly used in the generation of thermal power and smelting of iron ore. Coal occurs in rock sequences mainly of two geological ages, namely Gondwana and tertiary deposits. About 80 per cent of the coal deposits in India is of bituminous type and is of non-coking grade.
The most important Gondwana coal fields of India are located in Damodar Valley. Tertiary coals occur in Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya and Nagaland. Besides, the brown coal or lignite occurs in the coastal areas of Tamil Nadu, Pondicherry, Gujarat and Jammu and Kashmir.
- Petroleum:
Crude petroleum consists of hydrocarbons of liquid and gaseous states varying in chemical composition, colour and specific gravity. It is an essential source of energy for all internal combustion engines in automobiles, railways and aircraft. Its numerous by-products are processed in petrochemical industries such as fertilizer, synthetic rubber, synthetic fibre, medicines, Vaseline , lubricants, wax, soap and cosmetics. Petroleum is referred to as liquid gold because of its scarcity and diversified uses Lunej.
Mumbai High which lies 160 km off Mumbai was discovered in 1973 and production commenced in 1976. Oil and natural gas have been found in exploratory wells in Krishna-Godavari and Kaveri basin on the east coast. Oil extracted from the wells is crude oil and contains many impurities. It cannot be used directly. It needs to be refined. There are two types of refineries in India: (a) field based and (b) market based. Digboi is an example of field based and Barauni is an example of market based refinery. There are 18 refineries in India.
Do Check - Resources, Types And Development
- Natural Gas:
The Gas Authority of India Limited was set up in 1984 as a public sector undertaking to transport and market natural gas. It is obtained along with oil in all the oil fields but exclusive reserves have been located along the eastern coast as well as (Tamil Nadu, Orissa and Andhra Pradesh), Tripura, Rajasthan and off-shore wells in Gujarat and Maharashtra. Crude petroleum occurs in sedimentary rocks of the tertiary period. Oil exploration and production was systematically taken up after the Oil and Natural Gas Commission was set up in 1956. Till then, the Digboi in Assam was the only oil producing region but the scenario has changed after 1956.
In recent years, new oil deposits have been found at the extreme western and eastern parts of the country. Non-Conventional Energy Sources Fossil fuel sources, such as coal, petroleum, natural gas and nuclear energy use exhaustible raw materials. Sustainable energy resources are only the renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro geothermal and biomass. These energy sources are more equitably distributed and environmental friendly. The non-conventional energy sources will provide more sustained, eco-friendly cheaper energy after the initial cost is taken care of.
- Nuclear Energy Resources:
Nuclear energy has emerged as a viable source in recent times. Important minerals used for the generation of nuclear energy are uranium and thorium. Uranium deposits occur in the Dharwar rocks. Geographically, uranium ores are known to occur in several locations along the Singbhum Copper belt. It is also found in Udaipur, Alwar and Jhunjhunu districts of Rajasthan, Durg district of Chhattisgarh, Bhandara district of Maharashtra and Kullu district of Himachal Pradesh.
Thorium is mainly obtained from monazite and ilmenite in the beach sands along the coast of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. World’s richest monazite deposits occur in Palakkad and Kollam districts of Kerala, near Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh and Mahanadi river delta in Orissa. Atomic Energy Commission was established in 1948, progress could be made only after the establishment of the Atomic Energy Institute at Trombay in 1954 which was renamed as the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre in 1967.
- Solar Energy:
Sun rays tapped in photovoltaic cells can be converted into energy, known as solar energy. The two effective processes considered to be very effective to tap solar energy are photovoltaic and solar thermal technology. Solar thermal technology has some relative advantages over all other non-renewable energy sources. It is cost competitive, environment friendly and easy to construct.
Solar energy is 7 per cent more effective than coal or oil based plants and 10 per cent more effective than nuclear plants. It is generally used more in appliances like heaters, crop dryers, cookers, etc. The western part of India has greater potential for the development of solar energy in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- Wind Energy:
Wind energy is absolutely pollution free, inexhaustible source of energy. The mechanism of energy conversion from blowing wind is simple. The kinetic energy of wind, through turbines is converted into electrical energy. The permanent wind systems such the trade winds, westerlies and seasonal wind like monsoon have been used as source of energy. Besides these, local winds, land and sea breezes can also be used to produce electricity. India, already has started generating wind energy.
It has an ambitious programme to install 250 wind-driven turbines with a total capacity of 45 megawatts, spread over 12 suitable locations, especially in coastal areas. According to the estimation by Ministry of Power, India will be able to produce 3,000 megawatts of electric from this source. The Ministry of non-conventional sources of energy is developing wind energy in India to lessen the burden of oil import bill.
The country’s potential of wind power generation exceeds 50,000 megawatts, of which one fourth can be easily harnessed. In Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Karnataka, favourable conditions for wind energy exist. Wind power plant at Lamba in Gujarat in Kachchh is the largest in Asia. Another, wind power plant is located at Tuticorin in Tamil Nadu.
- Tidal and Wave Energy:
Ocean currents are the store-house of infinite energy. Since the beginning of seventeenth and eighteenth century, persistent efforts were made to create a more efficient energy system from the ceaseless tidal waves and ocean current. Large tidal waves are known to occur along the west coast of India. Hence, India has great potential for the development of tidal energy along the coasts but so far these have not yet been utilised.
- Geothermal Energy:
When the magma from the interior of earth, comes out on the surface, tremendous heat is released. This heat energy can successfully be tapped and converted to electrical energy. Apart from this, the hot water that gushes out through the geyser wells is also used in the generation of thermal energy. It is popularly known as Geothermal energy.
This energy is now considered to be one of the key energy sources which can be developed as an alternate source. The hot springs and geysers are being used since medieval period. In India, a geothermal energy plant has been commissioned at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh. The first successful (1890) attempt to tap the underground heat was made in the city of Boise, Idaho (U.S.A.), where a hot water pipe network was built to give heat to the surrounding buildings. This plant is still working.
- Bio-Energy:
Bio-energy refers to energy derived from biological products which includes agricultural residues, municipal, industrial and other wastes. Bioenergy is a potential source of energy conversion. It can be converted into electrical energy, heat energy or gas for cooking. It will also process the waste and garbage and produce energy.
This will improve economic life of rural areas in developing countries, reduce environmental pollution, enhance self-reliance and reduce pressure on fuel wood. One such project converting municipal waste into energy is Okhla in Delhi.
- Conservation of Mineral Resources:
The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of quest for economic development with environmental concerns. Traditional methods of resource use result into generating enormous quantity of waste as well as create other environmental problems. Hence, for sustainable development calls for the protection of resources for the future generations. There is an urgent need to conserve the resources.
The alternative energy sources like solar power, wind, wave, geothermal energy are inexhaustible resource. These should be developed to replace the exhaustible resources.
In case of metallic minerals, use of scrap metals will enable recycling of metals. Use of scrap is specially significant in metals like copper, lead and zinc in which India’s reserves are meager. Use of substitutes for scarce metals may also reduce their consumption. Export of strategic and scarce minerals must be reduced, so that the existing reserve may be used for a longer period.
Uses of Minerals:
Minerals are used in many industries. Minerals which are used for gems are usually hard. These are then set in various styles for jewellery. Copper is used in everything from coins to pipes. Silicon, used in the computer industry is obtained from quartz. Aluminium obtained from its ore bauxite is used in automobiles and airplanes, bottling industry, buildings and even in kitchen cookware.
Do Check - The Indian Constitution
Conservation of Minerals
Minerals are a non-renewable resource. The rate of formation is much smaller than the rate at which the humans consume these minerals. It is necessary to reduce wastage in the process of mining. Recycling of metals is another way in which the mineral resources can be conserved.
Ways to Conserve Minerals:
- Recycling -It means using discarded materials once again. Many metals like Iron, Gold, Copper and Aluminium become reusable through recycling.
- Avoid Wastage - Minerals can be conserved by using efficient methods of extraction and processing and by avoiding wastage. Saving can be done at consumption level also.
- Substitutes - In recent year's biodegradable plastics and other substitutes have been used to conserve mineral resources.
Power Resources
Energy is an indispensable requirement in modern life. It may be manual or animal and mechanical or electrical. Electricity is used to operate various kinds of machines. Availability of energy is a pre-requisite of modern economic activities. There are several sources of energy: some of them are coal, petroleum, natural gas, solar energy, wind energy and hydel energy. Sources of energy are categorised as conventional and non-conventional. Conventional sources of energy are those which have been in common use for a long time. Firewood and fossil fuels are the two main conventional energy sources.
- Firewood:
It is widely used for cooking and heating. In our country more than fifty per cent of the energy used by villagers comes from fire wood. Fossil fuel such as coal, petroleum and natural gas are the main sources of conventional energy. The reserves of these minerals are limited and are likely to be exhausted soon.
- Coal:
This is the most abundantly found fossil fuel. It is used as a domestic fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines and to generate electricity. Electricity from coal is called thermal power. Coal is often referred to as Buried Sunshine. The leading coal producers are China, USA, Germany, Russia, South Africa and France. In India coal producing are Raniganj, Jharia, Dhanbad and Bokaro in Jharkhand.
- Petroleum:
It is found between the layers of rocks and is drilled from oil fields located in off-shore and coastal areas. When refined it produces a variety of process like diesel, petrol, kerosene, wax, plastics and lubricants. The chief petroleum producing countries are Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Qatar. The other major producers are USA, Russia Venezuela, and Algeria. The leading producers in India are Digboi in Assam, Bombay High in Mumbai and the deltas of Krishna and Godavari rivers.
- Natural Gas:
Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits and is released when crude oil is brought to the surface. It can be used as a domestic and industrial fuel. Russia, Norway, UK and the Netherlands are the major producers of natural gas. In India Jaisalmer, Krishna Godavari delta, Tripura and some areas off shore in Mumbai have natural gas resources.
- Hydel Power:
River water from a dam is made to fall over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam. The moving blades then turn the generator to produce electricity. This is called hydro electricity. One fourth of the world's electricity is produced by hydel power. The leading producers of hydel power in the world are Paraguay, Norway, Brazil and China. Some important hydel power stations in India are Bhakra Nangai, Gandhi Sagar, Nagarjunsagar and Damodar valley projects.
Do Check - Human Resources
Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
The increasing use of fossil fuels is leading to its shortage. It is estimated that if the present rate of consumption continues, the reserves of these fuel will get exhausted. Moreover, their use also causes environmental pollution. Therefore, there is need for using non- conventional sources such as solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy which are renewable.
- Solar Energy
Solar energy trapped from the sun can be used in solar cells to produce electricity for heating and lighting purpose. The technology of utilising solar energy benefits a lot of tropical countries that are blessed with abundant sun shine. Solar energy is also used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers besides being used for community lighting and traffic signals.
.png)
- Wind Energy:
Wind is an inexhaustible source of energy. Wind mills have been used for grinding grain and lifting water since times immemorial. In modern time wind mills, the high speed winds rotate the wind mill which is connected to a generator to produce electricity. Windfarms are found in Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, UK, USA and Spain are noted for their wind energy production.
.png)
- Nuclear power
Nuclear power is obtained from energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radio active elements like uranium and thorium. These fuels undergo nuclear fission in nuclear reactors and emit power. The greatest producers of nuclear power are USA and Europe. In India Rajasthan and Jharkhand have large deposits of Uranium.
Thorium is found in large quantities in the Monozite sands of Kerala. The nuclear power stations in India are located in Kalpakkam in Tamilnadu, Tarapur in Maharastra, Ranapratap Sagar near Kota in Rajasthan, Narora in Uttar Pradesh and Kaiga in Karnataka.

- Geothermal Energy:
Heat energy obtained from the earth is called geothermal energy.
Geothermal energy in the form of hot springs has been used for cooking, heating and bathing for several years. USA has the world's largest geothermal power plants followed by New Zealand, Iceland, Philippines and Central America. In India, geothermal plants are located in Manikarna in Himachal Pradesh and Puga valley in Ladakh.

- Tidal Energy
Energy generated from tides is called tidal energy. Tidal energy can be harnessed by building dams at narrow openings of the sea. During high tide the energy of the tides is used to turn the turbine installed in the dam to produce electricity. Russia, France and the Gulf of Kachchh in India have huge tidal mill farms.

- Biogas:
Organic waste such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung and kitchen waste can be converted into a gaseous fuel called biogas. Biogas is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting and pithing and produces huge amount of organic manure each year.

Conservation of Sources of Energy
- Conservation is possible by making use of renewable sources of energy.
- Use energy in a planned way.
- Burning of waste to generate power.
- General increase in power efficiency of machinery and appliances.
- Increase in power station efficiency.
Do You Know?
- The salt in your food and graphite in your pencil are also minerals.
- A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals but without definite composition of constituent of mineral. Rocks from which minerals are mined are known as ores. Although more than 2800 types of minerals have been identified, only about 100 are considered ore minerals. Thus one can easily notice that all minerals are rocks but all rocks are not minerals.
- You can always tell if a rock contains copper because then the rock looks blue in colour.
- Switzerland has no known mineral deposit in it.
- A green diamond is the rarest diamond.
- The oldest rocks in the world are in Western Australia. They date from 4300 million years ago, only 300 million years after the earth was formed.
- The word petroleum is derived from Latin words - Petra meaning rock, oleum meaning oil. So, petroleum means rock oil.
- Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a popular eco-friendly automobile fuel as it causes less pollution than petroleum and diesel.
- Norway was the first country in the world to develop hydroelectricity.
- The site of the world's first solar and wind powered bus shelter is in Scotland.
Exercise
- Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of minerals?
(A) They are created by natural processes.
(B) They have a definite chemical composition.
(C) They are inexhaustible
(D) Their distribution is uneven.
- Which one of the following is NOT a producer of mica?
(A) Jharkhand
(B) Rajasthan
(C) Karnataka
(D)Andhara Pradesh
- Which one of the following is a leading producer of copper in the world?
(A) Bolivia
(B) Chile
(C) Ghana
(D) Zimbabwe
- Which one of the following practices will NOT conserve LPG in your kitchen?
(A) Soaking the dal for some time before cooking it.
(B) Cooking food in a pressure cooker.
(C) Keeping the vegetable chopped before lighting the gas for cooking.
(D) Cooking food in an open pan kept on low flame.
- Which is a non metallic mineral?
(A) Zirconium
(B) Bauxite
(C) Lead
(D) Diamond
- Limestone is found in:
(A) Sedimentary rocks
(B) Metamorphic rocks
(C) Igneous rocks
(D) Place deposits
- Reserves of Copper in India are found at:
(A) Madhya Pradesh
(B) Jharkhand
(C) Gujarat
(D) Maharashtra
- Most of the energy consumed in the world today is produced by?
(A) Mineral oil
(B) Wind
(C) Water
(D) Solar
- Which country has the largest reserves of Mineral oil?
(A) Mexico
(B) Libya
(C) Saudi-Arabia
(D) Nigeria
- How much world's electricity is produced by hydel power?
(A)1/3
(B) 1/4
(C)1/2
(D) 1/5
Subjective Questions
- What are minerals?
- Name the source of power.
- What is a mine?
- List three alternative source of energy .
- What is recycling?
- Why are coal, mineral oil and natural gas called fossil fuels?
- What are metallic minerals?
- Which countries are the largest consumer of copper, Aluminium and Nickel?
- What is solar energy? How can it be trapped?
- Explain what is meant by placer deposits?
- What is geothermal energy? Where is the geothermal plant set up in India?
- Describe the three basic ways through which energy is obtained.
- Distinguish between biogas and natural gas.
- Give reasons - Petroleum is referred to as "black gold".
- Quarrying can become a major environmental concern-comment.
- What are conventional sources of energy?
- How can we conserve the mineral and power resources?
- Write a note on non conventional sources of energy.
- Distinguish between metallic and nonmetallic minerals.
- Write in brief the conservation of mineral and power resources.
Answers to Exercise
- (C)
- (C)
- (B)
- (D)
- (D)
- (A)
- (B)
- (A)
- (C)
- (B)