Distance–time graph for non-uniform motion
We already know that for a uniform motion, the distance-time graph is a straight line. This is because a body in uniform motion covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
Now if a body is undergoing non-uniform motion, the body covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. This makes the distance-time graph non-linear.
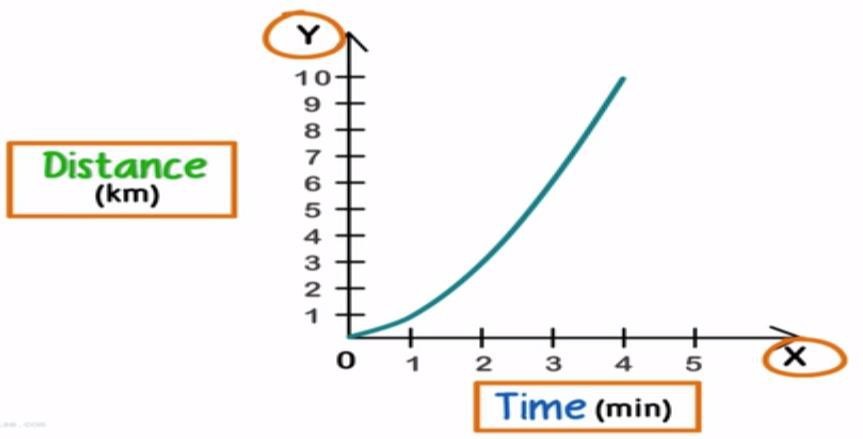
Distance-time graph for non-uniform motion
How to find the distance traveled by a body in non-uniform motion?
To find the distance traveled by the body at any time instant, we will mark a point corresponding to that time on the X-axis, on the graph. Mapping this point towards the Y-axis, we can find the distance travelled by that body.
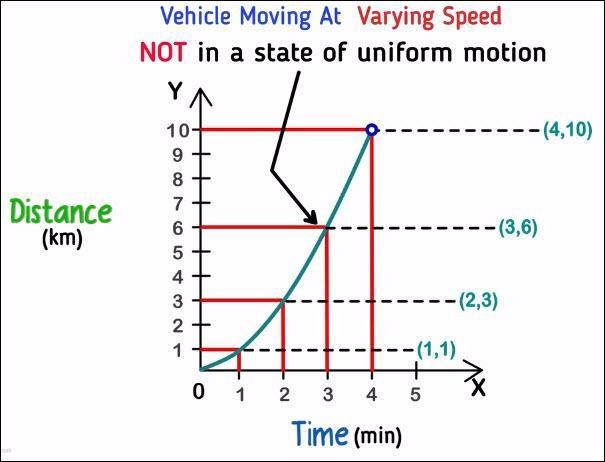
Non-uniform motion example
From this graph, we can say that distance travelled by the vehicle in 1 minute is 1 kilometer, in 2 minutes it is 3 kilometers, in 3 minutes it is 6 kilometers and so on.
How to find the speed of a body in non-uniform motion?
Using the same graph as above, let us calculate the speed of the vehicle at 4 minutes.
Being a non-linear graph, we cannot find the slope of this graph. To calculate the speed of a body in non-uniform motion, all we need to do is apply the formula of speed for that instant of time.
From the graph, we can see that 4 minute on the X-axis corresponds to 10 kilometers on the Y- axis.
Substituting the values, we get,
𝑆𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 =10 𝑘𝑚/4 𝑚𝑖𝑛
=2.5 x km/min
This speed is not the constant speed of that vehicle in non-uniform motion, but the variable speed calculated at that instant of time.
