How do Acids react with metal carbonates?
Sodium carbonate (𝑁𝑎2𝐶𝑂3)is an example of a metal carbonate.
Let us understand how acids react with sodium carbonate with the help of an experiment.
Things needed:
- A stand
- A cork
- Two test tubes
- A delivery tube
- Thistle funnel
- Dilute hydrochloric acid
- Sodium carbonate
- Calcium hydroxide solution (Lime water)
Procedure:
- Add half a gram of sodium carbonate to a test
- In this test tube, add dilute hydrochloric acid. Some gas is
- In the other test tube, add calcium hydroxide solution or lime water (Ca(OH)_{2}).
- Connect both the test tubes with a delivery
- The gas produced in the first test tube is passed to the second test tube with the help of the delivery tube. Lime water turns
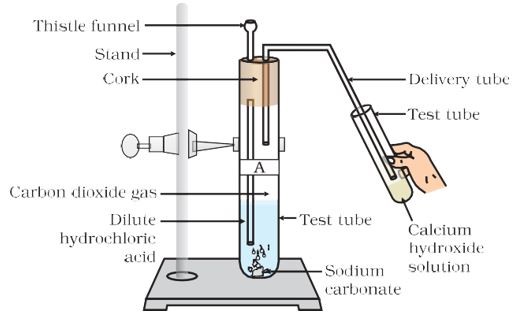
Reaction of Dilute hydrochloric acid with Sodium carbonate
Observation:
- When hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium chloride, carbon dioxide gas is released. The reaction is
𝑵𝒂𝟐𝑪𝑶𝟑(𝒔) + 𝟐𝑯𝑪𝒍(𝒂𝒒) → 𝟐𝑵𝒂𝑪𝒍(𝒂𝒒) + 𝑪𝑶𝟐(𝒈) + 𝑯𝟐𝑶(𝒍)
- When lime water turns milky, it confirms the evolution of carbon dioxide The reaction is
𝑪𝒂(𝑶𝑯)𝟐(𝒂𝒒) + 𝑪𝑶𝟐(𝒈) → 𝑪𝒂𝑪𝑶𝟑(𝒔) + 𝑯𝟐𝑶(𝒍)
(Lime water) (White precipitate)
- The white precipitate is calcium When excess carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it makes the milky colour of lime water disappear because of the formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate which is soluble in water. The reaction is
Conclusion:
𝑪𝒂𝑪𝑶𝟑(𝒔) + 𝑯𝟐𝑶(𝒍) + 𝑪𝑶𝟐(𝒈) → 𝑪𝒂(𝑯𝑪𝑶𝟑)𝟐(𝒂𝒒)
(Soluble in water)
- Acids react with metal carbonates to give salt, carbon dioxide, and
This can be generalized as
Metal carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
How do Acids react with metal hydro-carbonates?
The reaction of acids with metal hydrogen carbonates also gives salt, carbon dioxide, and water. The reaction is
𝑵𝒂𝑯𝑪𝑶𝟑(𝒔) + 𝑯𝑪𝒍(𝒂𝒒) → 𝑵𝒂𝑪𝒍(𝒂𝒒) + 𝑪𝑶𝟐(𝒈) + 𝑯𝟐𝑶(𝒍)
Thus, all the metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates react with acids to give a corresponding salt, carbon dioxide, and water. This can be generalized as
