About Geometry Formulas
Geometry formulae are used to calculate geometric shape dimensions, perimeter, area, surface area, volume, and so on. Geometry is a branch of mathematics that studies the links between points, lines, angles, surfaces, measurements, and properties of solids. Geometry is divided into two types: 2D or plane geometry and 3D or solid geometry. 2D shapes, such as squares, circles, and triangles, are flat shapes with only two dimensions: length and width. 3D objects, such as a cube, cuboid, sphere, cylinder, or cone, have three dimensions: length, width, and height or depth.
Geometry formulae are used to calculate the dimensions, perimeter, area, surface area, volume, and other properties of 2D and 3D geometric shapes. 2D shapes include flat shapes such as squares, circles, and triangles, while 3D shapes include cube, cuboid, sphere, cylinder, cone, and others. The following are the basic geometry formulas:
Square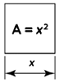 |
Triangle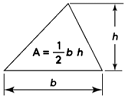 |
Circle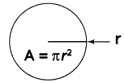 |
Rectangle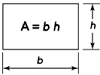 |
Eclipse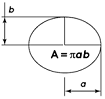 |
Trapezoid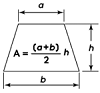 |
List of Geometry Formulas
- Perimeter of a Square = 4(Side)
- Perimeter of a Rectangle = 2(Length + Breadth)
- Area of a Square = Side2
- Area of a Rectangle = Length × Breadth
- Area of a Triangle = ½ × base × height
- Area of a Trapezoid = ½ × (base1+base2)(base1+base2)× height
- Area of a Circle = A = π×r2
- Circumference of a Circle = 2πr
- Curved surface area of a Cylinder = 2πrh
- Total surface area of a Cylinder = 2πr(r + h)
- Volume of a Cylinder = V = πr2h
- The curved surface area of a cone = πrl
- Total surface area of a cone = πr(r+l) = πr[r+√(h2 + r2)]
- Volume of a Cone = V = ?×πr2h
- Surface Area of a Sphere = S = 4πr2
- Volume of a Sphere = V = 4/3×πr3
Where,
- r = Radius
- h = Height, and
- l = Slant height
|
SHAPES |
FORMULAS |
|
1. Right Triangle |
Pythagoras Theorem: a2 + b2 = c2 Area = ½ ab Perimeter = a + b + √(a2 + b2) Where, a = altitude of a triangle b = base of a triangle |
|
2. Triangle |
Perimeter, P = a + b + c Area, A = ½ bh Height, h = 2(A/b) Where, a,b,c are three sides of a triangle. |
|
3. Rectangle |
Perimeter = 2(l + w) Area = lw Diagonal, d = √(l2 + w2) Where, l = length of a rectangle w = width of a rectangle |
|
4. Parallelogram |
Perimeter, P = 2(a + b) Area, A = bh Height, h = A/b Base, b = A/h Where, a & b are the sides of a parallelogram h = height of a parallelogram |
|
5.Trapezium |
Area, A = ½(a + b)h Height, h = 2A/(a + b) Base, b = 2(A/h) – a Where, a & b are the parallel sides h = distance between two parallel sides |
|
6. Circle |
Circumference = 2πr Area = πr2 Diameter = 2r Where, r = radius of a circle |
|
7. Square |
Perimeter, P = 4a Area, A = a2 Diagonal, d = a√2 Side, a = √A = d/2√2 Where, a = side of a square |
|
8. Arc |
Arc Length, L = rθ Area, A = ½r2θ Here, θ is the central angle is radians. Where, r = radius |
|
9. Cube |
Area, A = 6a2 Volume, V = a3 Edge, a = V? Space diagonal = a√3 Where, a = side of a cube |
|
10. Cuboid |
Surface Area, A = 2(lb + bh + hl) Volume, V = lbh Space diagonal, d = √( l2 + b2 +h2) Where, l = length b = breath h = height |
|
11. Cylinder |
Total Surface Area(TSA), A = 2πrh + 2πr2 Curved Surface Area (CSA), Ac = 2πrh Volume, V = πr2h Base Area, Ab = πr2 Radius, r = √(V/πh) Where, r = radius of a cylinder h = height of a cylinder |
|
12. Cone |
Total Surface Area(TSA), A = πr(r+l) = πr[r+√(h2+r2)] Curved Surface Area (CSA), Ac = πrl Volume, V = ?πr2h Slant Height, l = √(h2+r2) Base Area, Ab = πr2 Where, r = radius of a cone h = height of a cone l = slant height |
|
13. Sphere |
Surface Area, A = 4πr2 Volume, V = ?⁄?πr3 Diameter = 2r Where, r = radius of a sphere |
Get the list of all Maths formulas used in general calculations.