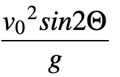About Trajectory Formula
When a body is thrown in air, it travels a curved path under the action of the Force of gravity. This curved path followed by the body is called it’s trajectory and the body so thrown is known as a Projectile. We also refer to it as Projectile Motion. Get the List of all Maths formulas in one place.
Some common examples of Trajectory motion are a bullet fired from a gun, an athlete throwing a javelin, a football kicked up in the air.
A Trajectory formula relates the vertical(y) and horizontal(x) position of the particle when thrown in air under the action of Gravitational force. If we launch the Projectile with an initial velocity v0, at angle ? from the horizontal plane. We can find the vertical position of the object from the horizontal position using this Formula:
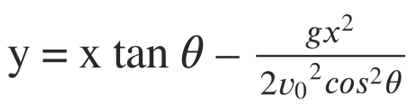
y = refers to the vertical position of the object.
x = refers to the horizontal position of the object.
?0 = refers to the initial velocity of the object
g = acceleration due to the gravity given by 9.8 ?/?2
? =refers to the initial angle from the horizontal plane in degrees or radians.
Some terms related to the Projectile Motion:
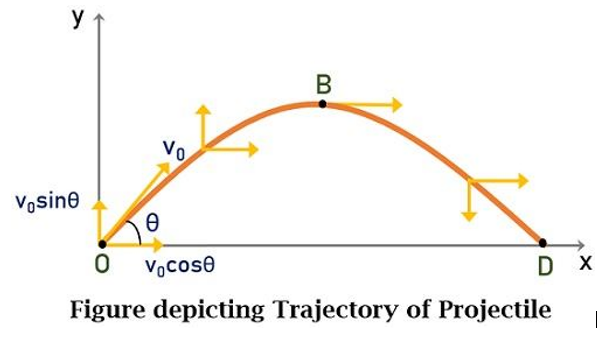
- Time of flight(T)- It is defined as the time taken by the projectile to complete the entire journey. It is the time from when the object is projected to the time it reaches the surface.
- Maximum height(H)-At a certain point on the path of the projectile, the vertical component of it’s velocity becomes zero.From this point, the vertical velocity vector goes downwards.The vertical position of the projectile at this point is equal to it’s Maximum height.
- Horizontal Range(R) - Range is the maximum horizontal distance covered by the projectile throughout it’s Motion.
Time of Flight,T = 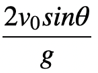
Maximum Height Reached, H = 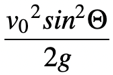
Horizontal Range, R =