In the realm of geometry, complementary angles play a significant role. These angles are fundamental in understanding various geometric concepts and solving related problems. This guide will delve into the definition, properties, and theorems associated with complementary angles, providing a detailed overview for learners and enthusiasts alike.
What Are Complementary Angles?
Complementary angles are two angles that, when added together, sum up to 90 degrees. This is the defining characteristic of complementary angles. For example, if one angle measures 60 degrees and another measures 30 degrees, they are complementary because 60° + 30° = 90°.
Definition of Complementary Angles
In geometry, two angles are termed complementary if their angle measures add up to exactly 90 degrees. For instance:
A 60° angle and a 30° angle are complementary.
Conversely, the complement of a 30° angle is a 60° angle, and the complement of a 60° angle is a 30° angle.
Types of Complementary Angles
Complementary angles can be categorized based on their spatial arrangement. The two main types are:
1. Adjacent Complementary Angles
Adjacent complementary angles are two angles that share a common vertex and side but do not overlap. Together, they form a right angle.
2. Non-Adjacent Complementary Angles
Non-adjacent complementary angles are two angles that are not next to each other but still add up to 90 degrees. These angles are separate and do not share a common vertex or side.
Diffrence Between area and Volume
How to Find the Complement of an Angle
To determine the complement of an angle, subtract the given angle from 90 degrees. The formula is:
Complement
For example, to find the complement of a 57° angle: 90°−57°= 33°
Key Properties of Complementary Angles
Understanding the properties of complementary angles helps in recognizing their applications in geometric problems. Here are some essential properties:
- Sum Property: The sum of two complementary angles is always 90 degrees.
- Position: Complementary angles can be adjacent or non-adjacent.
- Three Angles: Three angles cannot be considered complementary if their sum is 90 degrees; only pairs of angles can be complementary.
- Right-Angled Triangle: The two acute angles in a right-angled triangle are always complementary.
Complementary Angles vs. Supplementary Angles
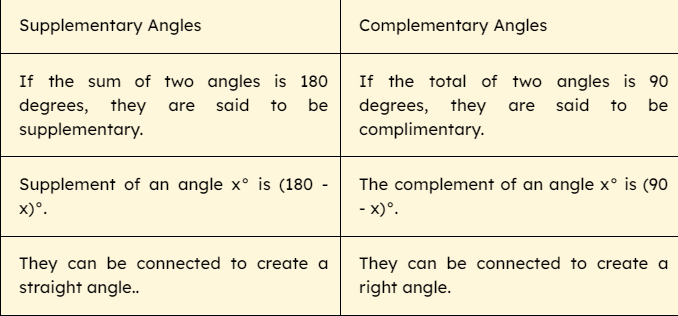
The Complementary Angles Theorem
The Complementary Angles Theorem states that if two angles are complementary to the same angle, they are also complementary to each other. This theorem can be illustrated as follows:
Proof of the Complementary Angles Theorem
Consider the following geometric scenario to prove the theorem:
Let angle ∠POQ be complementary to both ∠AOP and ∠QOR. According to the theorem:
- ∠POQ+∠AOP=90°
- ∠POQ+∠QOR=90°
By subtracting ∠POQ from both sides of these equations:
∠AOP=∠QOR
Thus, the angles ∠AOP and ∠QOR are congruent, verifying the theorem.
Conclusion
In summary, complementary angles are a fundamental concept in geometry defined by their sum of 90 degrees. Understanding the difference between complementary and supplementary angles, recognizing the properties of complementary angles, and learning theorems like the Complementary Angles Theorem are crucial for mastering geometric principles.
Feel free to explore these concepts further through practice problems and geometric proofs.