Differential calculus is a part of math focused on finding the derivative of a function. It studies how quantities change in relation to other variables. Finding a function's derivative is called differentiation.
Introduction Calculus and Approximation
Differential calculus is a part of mathematics focused on finding a function's derivative. It examines how quantities change in relation to other variables. The process of finding a derivative is called differentiation. Essentially, differential calculus involves breaking things down to see how they change.
A differential equation involves the derivative of a dependent variable with respect to an independent variable, such as dydx = f(x), where x is the independent variable and y is the dependent variable.
Also Check: Difference Between Variance and Standard Deviation
Derivatives are useful for:
- Calculating the rate of change of quantities.
- Finding the equations of tangent and normal lines to a curve at a point.
- Identifying turning points on a graph to find maximum or minimum values.
- Determining intervals where a function increases or decreases.
- Estimating approximate values of various quantities.
For example, to find the rate of change of a circle's area (A = πr2) with respect to its radius (r) when r is 5 cm:
dA/dr = d/dr(πr2) = 2πr
When r = 5 cm:
dA/dr = 2π × 5 = 10π
Differential Calculus Approximations
Differentials can approximate quantities. Let f(x) be a function. If x increases by a small amount Δx, the corresponding change in y is Δy = f(x + Δx) - f(x) as illustrated in the figure below.
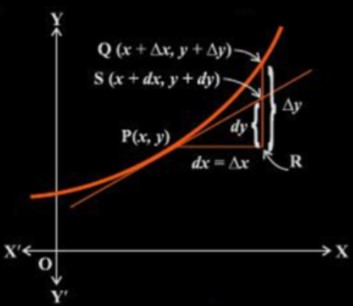
Based on the previous discussion:
- The differential of x, denoted as dx, is dx = x.
- The differential of y, denoted as dy, is dy = f'(x)dx = (dy/dx)x.
- If dx is very small compared to x, then dy closely approximates y.
Also Check: Difference Between Variance and Standard Deviation
Example of Differential Calculus and Approximation
To approximate 25.5 using a differential:
- Let y = x, where x = 25 and dx = 0.5.
Then,
- dy = f'(x)dx = 1 × 0.5 = 0.5.
So, the approximate value of 25.5 is:
- 25 + 0.5 = 25.5.
Conclusion
Differential calculus helps calculate how one quantity changes in relation to another. The rate of change of x relative to y is denoted by dx/dy. It is a key concept in calculus alongside integrals.