About Heron’s Formula – Class 9 Maths
The class-9 maths notes for the Chapter-Heron’s Formula chapter teaches students how to find the area of triangles using their sides. Our Class 9 maths notes make it simple to understand each step of the derivation and application of the formula. With NCERT solutions for class 9 Maths, students can solve various exercises involving real-life problems, from land area calculations to geometry-based applications.
Our Class 9 Maths tuition focuses on concept reinforcement through practical examples and quizzes. Tutors help students memorise the formula efficiently and apply it accurately in problem-solving scenarios, boosting confidence and exam performance.
Mensuration
A branch of mathematics which concerns itself measurement of lengths, areas and volumes of plane and solid figure is called Mensuration.
Perimeter
The perimeter of a plane figure is the length of its boundary. In case of a triangle or a polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its sides.
Units of Perimeter
The unit of perimeter is the same as the unit of length i.e. centimetre (cm), metre(m), kilometere (k m) etc.
| Measurement | Conversion |
| 1 centimetre (cm) | = 10 milimetre (mm) |
| 1 decimetre (dm) | = 10 centrimetre |
| 1 metre (m) | = 10 decimetre = 100 centimetre = 1000 milimetre |
| 1 decamete (dam) | = 10 metre = 1000 centimetre |
| 1 hectometre (hm) | = 10 decametre = 100 metre |
| 1 kilometre (km) | = 1000 metre = 100 decametre = 10 hectometre |
Area of Triangle with Given Base and Height
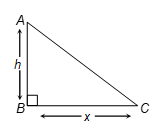
Area of Right-Angled Triangle
Let ABC right-angled triangle, right-angled at B then
Area = (1/2) × (BC) × (AB)
A = (1/2) × x × h
where x is the base and h is the height
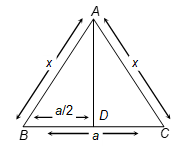
Area of Isosceles Triangle
Let ABC be an isosceles triangle such that AB = AC = x and BC = a, then
Area = (1/2) × (base) × (height)
Area = (1/2) × (BC) × (AD)
In △ABD, ∠D = 90° so, by Pythagoras theorem,
AD = √(x² - a²/4)
Area = (1/2) × a × √(x² - a²/4)
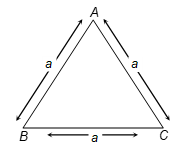
Area of Equilateral Triangle
Let ABC be an equilateral triangle with each side equal to 'a'
Area = (√3/4) × (side)²
A = (√3/4) × a²
Example 1: Find the area of a triangle with base = 10 cm and height 5 cm.
Solution:
Area of a triangle is (1/2) × b × h where b = base = 10 cm and h = height = 5 cm
A = (1/2) × 10 × 5 cm²
A = 25 cm²
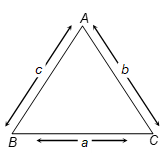
Area of Triangle by Heron's Formula
The formula given by Heron about the area of a triangle is also known as Heron's formula. It is given by
Area of a triangle = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
where a, b, c are the sides of a triangle and s is the semi-perimeter
i.e., s = (a + b + c)/2
Example 2: Find the area of a triangle whose sides are 13 cm, 14 cm and 15 cm.
Solution:
If a, b, c are the sides of a triangle and s is the semi-perimeter, then its area is given by
A = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
Here, a = 13 cm, b = 14 cm and c = 15 cm
∴ s = (1/2)(a + b + c) = (1/2)(13 + 14 + 15) = 21 cm
A = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
= √[21(21-13)(21-14)(21-15)]
A = √21876 = √(7²×3²×8²×3) = 7×4×3
A = 7 × 4 × 3 = 84 cm²
Application of Heron's Formula in Finding areas of Quadrilaterals
Heron's formula can be applied to find the area of a quadrilateral by dividing the quadrilateral into two triangular parts.
Example 3: A rhombus shaped field has green grass for 18 cows to graze. If each side of the rhombus is 30 m and its longer diagonal is 48 m, how much area of grass field will each cow be grazing?
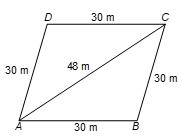
Solution:
s = (30 + 30 + 48)/2 = 54 m
Area of △ABC = Area of △ADC
= √[54(54 - 30)(54 - 30)(54 - 48)] m²
= √(54 × 24 × 24 × 6) m²
= 432 m²
So, Area of rhombus ABCD = 2 × Area of △ABC
= (2 × 432) m² = 864 m²
∴ Area of grass field each cow will graze = 864/18 m² = 48 m²
Example 4: A floral design on a floor is made up of 16 tiles, which are triangular, the sides of the triangle being 9 cm, 28 cm and 35 cm. Find the cost of polishing the tiles at the rate of 50 paise per cm².
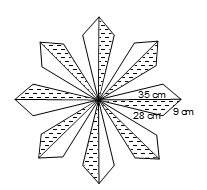
Solution:
Let s be the semi-perimeter of a tile. Then,
s = (28 + 9 + 35)/2 cm = 36 cm
∴ Area of one tile = √[36(36 - 28)(36 - 9)(36 - 35)] = 36√6 m²
∴ Area of 16 tiles = 16 × 36√6 cm² = 576√6 cm²
Hence, cost of polishing the tiles at the rate of 50 paisa i.e. Re (1/2) per cm²
= Rs (576√6 × 1/2) = Rs 705.45
Summary - Heron's Formula
Area of a triangle by Heron's formula
Area of a triangle = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)]
where a, b, c are the sides of a triangle and S is the semi-perimeter
i.e., S = (a + b + c)/2
Applications of Heron's formula in finding area of a quadrilateral
Heron's formula can be applied to find the area of a quadrilateral by dividing the quadrilateral into two triangular parts. If we join any of the two diagonals of the quadrilateral, then we get two triangles. Area of each triangle is calculated and the sum of two areas is the area of the quadrilateral.
Area of triangle with given base and height
Area = (1/2) × base × height
➢ Area of right-angled triangle: (1/2) × h × x
where h is the length of altitude and x is the length of the base
➢ Area of isosceles triangle: AD = √(x² - a²/4)
where a is the length of the base and x is the length of the remaining sides.
➢ Area of equilateral triangle: A = (√3/4) × a²
where a is the length of the each side.
Questions
Ques 1. The area of a triangle is 30 cm². Find the base if the altitude exceeds the base by 7 cm.
Ques 2. The cost of turfing a triangle field at the rate of Rs. 45 per 100 m² is Rs. 900. Find the height, if double the base of the triangle is 5 times the height.
Ques 3. From a point in the interior of an equilateral triangle, perpendicular drawn to the three sides are 8 cm, 10 cm and 11 cm respectively. Find the area of the triangle.
Ques 4. The difference between the sides at right angles in a right-angled triangle is 14 cm. The area of the triangle is 120 cm². Calculate the perimeter of the triangle.
Ques 5. Find the percentage increase in the area of a triangle if its each side is doubled.
Ques 6. An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colours, each piece measuring 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm. How much cloth of each colour is required for the umbrella?
Answers:
- 12 cm
- 40 cm
- 486.1 cm²
- 60 cm
- 300%
- 1000√6 cm²
Detailed Solutions
Q1. The area of a triangle is 30 cm². Find the base if the altitude exceeds the base by 7 cm.
Solution:
Let base BC = x cm then altitude = (x + 7) cm
Area of △ABC = (1/2) × base × height
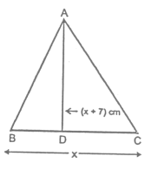
⇒ 30 = (1/2)(x)(x + 7)
⇒ 60 = x² + 7x
⇒ x² + 7x – 60 = 0
⇒ x² + 12x – 5x – 60 = 0
⇒ x(x + 12) – 5(x + 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 5) (x + 12) = 0
⇒ x = 5 or x = –12
⇒ x = 5 [∵ x ≠ –12]
∴ Base (x) = 5 cm and Altitude = x + 7 = 5 + 7 = 12 cm. Ans.
Q2. The cost of turfing a triangle field at the rate of Rs. 45 per 100 m² is Rs. 900. Find the height, if double the base of the triangle is 5 times the height.
Solution:
Let the height of triangular field be h metres.
It is given that 2 × (base) = 5 × (Height)
∴ Base = (5/2)h
Area = (1/2) × Base × Height
Area = (1/2) × (5/2)h × h = (5/4)h² ....(i)
∴ Cost of turfing the field is Rs. 45 per 100 m²
∴ Area = Total cost / Rate per sq. = 900 / (45/100) = 9000/45 = 2000 m² ....(ii)
From (i) and (ii)
(5/4)h² = 2000
⇒ 5h² = 8000
⇒ h² = 1600
⇒ h = 40 m
∴ Height of the triangular field is 40 cm. Ans.
Q3. From a point in the interior of an equilateral triangle, perpendicular drawn to the three sides are 8 cm, 10 cm and 11 cm respectively. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
Let each side of the equilateral △ABC = x cm,
From an interior point O, OD, OE and OF be drawn perpendicular to BC, AC and AB respectively. It is given that OD = 11 cm, OE = 8 cm and OF = 10 cm. Join OA, OB and OC.
Area of △ABC = Area of △OBC + Area of △OCA + Area of △OAB
= (1/2) × x × 11 + (1/2) × x × 8 + (1/2) × x × 10
= (29/2)x cm²
But, area of an equilateral triangle, whose each side is x
= (√3/4) × x² cm²
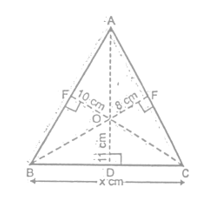
Therefore, (√3/4) × x² = (29/2)x
∴ x = (4 × 29)/(2 × √3) = 58/√3 cm
∴ Area of △ABC = (29/2) × (58/√3) cm² = 841/(1.73) cm²
∴ Area of △ABC = 486.1 cm² Ans.
Q4. The difference between the sides at right angles in a right-angled triangle is 14 cm. The area of the triangle is 120 cm². Calculate the perimeter of the triangle.
Solution:
Let the sides containing the right angle be x cm and (x – 14) cm.
The, its area = (1/2) × x × (x – 14) cm².
But, area = 120 cm² [Given]
∴ (1/2)x (x – 14) = 120
⇒ x² – 14x – 240 = 0
⇒ x² – 24x + 10x – 240 = 0
⇒ x(x – 24) + 10 (x – 24) = 0
⇒ (x – 24) (x + 10) = 0
⇒ x = 24 [Neglecting x = -10]
∴ one side = 24 cm, other side = (24 - 14) cm = 10 cm
Hypotenuse = √(24² + 10²) cm
= √(576 + 100) cm
= √576 cm
= 26 cm.
∴ Perimeter of the triangle = (24 + 10 + 26) c m = 60 cm. Ans.
Q5. Find the percentage increase in the area of a triangle if its each side is doubled.
Solution:
Let a, b, c be the sides of the given triangle and s be its semi-perimeter
∴ s = (1/2)(a + b + c) ....(i)
The sides of the new triangle are 2a, 2b and 2c.
Let s' be its semi-perimeter.
∴ s' = (1/2)(2a + 2b + 2c) = a + b + c = 2s [Using (i)]
Let Δ = Area of given triangle
Δ = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)] .....(ii)
And, Δ' = Area of new triangle
Δ' = √[s'(s'−2a)(s'−2b)(s'−2c)]
= √[2s(2s − 2a)(2s − 2b)(2s − 2c)] [Using (i)]
= √[16s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
Δ' = 4Δ
∴ Increase in the area of the triangle = Δ' – Δ = 4Δ – Δ = 3Δ
∴ % increase in area = (3Δ/Δ) × 100% = 300% Ans.
Q6. An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colours, each piece measuring 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm. How much cloth of each colour is required for the umbrella?
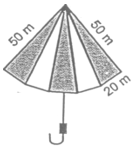
Solution:
The sides of a triangular piece are 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm
s = (a + b + c)/2 = (20 + 50 + 50)/2 = 60 cm = 60 cm
Area of one triangular piece
= √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[60(60 − 20)(60 − 50)(60 − 50)]
= √(60 × 40 × 10 × 10) = √24000
= 200√6 cm²
Area of cloth of each colour for five triangular pieces = 5 × 200√6 = 1000√6 cm²
Illustrations
Q1. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 4 cm.
Solution:
Area of equilateral triangle is (√3/4) × a²; where a = length of side
Area = (√3/4) × (4)² cm²
= (√3/4) × 16 cm²
= 4√3 cm²
Q2. Find the area of a triangle, two sides of which are 8 cm and 11 cm and the perimeter is 32 cm.
Solution:
Let a, b, c be the sides of the given triangle and 2s be its perimeter such that a = 8 cm, b = 11 cm and 2s = 32 cm i.e. s = 16 cm
Now, a + b + c = Perimeter
⇒ 8 + 11 + c = 32
⇒ c = 13
Hence, Area of given triangle = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[16 × 8 × 5 × 3] = 8√30 cm²
Q3. An isosceles triangle has perimeter 30 cm and each of the equal sides is 12 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
Let the length of the unequal side of given triangle be x cm.
∴ Perimeter = 30 cm
∴ x + 12 + 12 = 30
⇒ x + 24 = 30
⇒ x = 6
We have, 2s = 30 cm
∴ s = 15 cm
Hence, Area = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
⇒ Area = √[15(15 − 12)(15 − 12)(15 − 6)]
= √(15 × 3 × 3 × 9) = 9√15 cm²
Q4. The perimeter of a triangular field is 450m and its sides are in the ratio 13:12:5. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
Let the three sides be 13x, 12x and 5x
∴ Perimeter = 450
⇒ 13x + 12x + 5x = 450
⇒ 30x = 450
⇒ x = 15
So, the sides of the triangle are a = 13 × 15 = 195 m, b = 12 × 15 = 180 m and c = 5 × 15 = 75 m
It is given that perimeter = 450
⇒ 2s = 450
⇒ s = 225
⇒ Area = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[225(225 − 195)(225 − 180)(225 − 75)]
⇒ Area = √(225 × 30 × 45 × 150)
⇒ Area = √(5⁶ × 3⁶ × 2²) = 5³ × 3³ × 2 = 6750 m²
Q5. A traffic signal board, indicating 'SCHOOL AHEAD', is an equilateral triangle with side 'a'. Find the area of the signal board, using Heron's formula. If its perimeter is 180 cm, what will be the area of the signal board?
Solution:
Let 2s be the perimeter of the signal board. Then
2s = a + a + a ⇒ s = 3a/2
Area = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
⇒ Area = √[(3a/2)(3a/2 − a)(3a/2 − a)(3a/2 − a)]
⇒ Area = √[(3a/2) × (a/2) × (a/2) × (a/2)] = (√3/4)a²
∴ Perimeter = 180 cm
⇒ 3a = 180 or a = 60
∴ Area = (√3/4)(60)² = 900√3 cm²
Q6. The triangular side walls of a flyover have been used for advertisements. The sides of the walls are 122 m, 22 m and 120 m. The advertisements yield an earning of Rs. 5000 per m² per year. A company hired both walls for 3 months. How much rent did it pay?
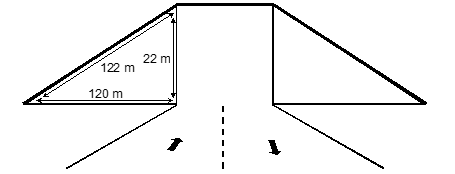
Solution:
The length of the sides of the walls are 122m, 22 m and 120 m.
As 122² = 120² + 20²
∴ Walls are in the form of right triangles.
∴ Area of two walls = 2 × [(1/2) × Base × Height]
⇒ Area of two walls = 2 × [(1/2) × 120 × 22] = 2640 m²
∴ Yearly rent = Rs 5000 per m² [given]
∴ Monthly rent = Rs(5000/12) per m²
Hence, rent paid by the company for 3 months = Rs[(5000/12) × 3 × 2640]
= Rs 3300000.
Q7. There is a slide in a park. One of its sidewalls has been painted in some colour with a message "KEEP THE PARK GREEN AND CLEAN". If the sides of the wall are 15 m, 11 m and 6 m, find the area painted in colour.
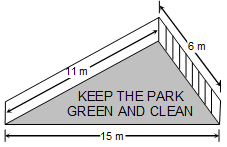
Solution:
Sidewall is in the triangular form with sides a = 15 m, b = 6 m and c = 11 m.
Let 2s be the perimeter of the sidewall. Then,
⇒ s = (15 + 11 + 6)/2
⇒ s = 32/2 = 16
∴ s − a = 16 − 15 = 1, s − b = 16 − 6 = 10
and s − c = 16 − 11 = 5
Hence, Area to be painted in colour = Area of the side wall
= √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √(16 × 1 × 10 × 5) = 20√2 m²
Q8. Find the area of a triangle having perimeter 32 cm, one side 11 cm and difference of other two sides is 5 cm.
Solution:
Let a, b and c be the three sides of △ABC
∴ a = 11
∴ a + b + c = 32 cm
⇒ 11 + b + c = 32 cm
or b + c = 21 cm ...(i)
∴ b − c = 5 cm [given] ...(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii), 2b = 26 cm
or b = 13 cm
∴ c = 21 – b [from (i)]
∴ c = 21 – 13 = 8 cm
Now, s = (a + b + c)/2 = 32/2 = 16 cm
Area of △ABC = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √(16 × 5 × 3 × 8) cm²
= √(64 × 30) cm² = 8√30 cm²
Q9. A triangular park in a city has dimensions 100 m × 90 m × 110 m. A contract is given to a company for planting grass in the park at the rate of Rs. 4000 per hectare. Find the amount to be paid to the company. (√2 = 1.414) (one hectare = 10,000 m²).
Solution:
Sides of the triangular park having lengths a = 100 m, b = 90 m and c = 110 m.
∴ s = (100 + 90 + 110)/2 = 150 m
Area of the triangular park = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √(150 × 50 × 60 × 40) m²
= √(900 × 10000 × 2) m² = 3000√2 m²
= 3000 × 1.414 m² = 4242 m²
= 4242/10000 hectares
⇒ = 0.4242 hectare
Amount paid for planting grass = 0.4242 × Rs. 4000 = Rs. 1696.80
Q10. A triangular park ABC has sides 120 m, 80 m and 50 m. A gardener has to put a fence all around it and also plant grass inside. How much area does he need to plant? Find the cost of fencing it with barbed wire at the rate of Rs 20 per metre leaving a space 3 m wide for a gate on one side.
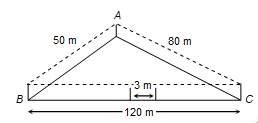
Solution:
s = (50 + 120 + 80)/2 = 250/2 = 125 m
Therefore, area of the park = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[125(125 − 120)(125 − 80)(125 − 50)]
= √(125 × 5 × 45 × 75) m²
= 375√15 m²
Perimeter of the park = AB + BC + CA = 250 m
Space to be left for gate = 3m
Therefore, length of the wire needed for fencing = 250 m − 3m = 247m
∴ Cost of fencing = Rs 20 × 247 = Rs 4940.
Q11. A farmer has a triangular field with sides 240 m, 200 m, 360 m, where she grew wheat. In another triangular field with sides 240 m, 320 m, 400 m adjacent to the previous field, she wanted to grow potatoes and onions. She divided the field in two parts by joining the mid-point of the longest side to the opposite vertex and grew potatoes in one part and onions in the other part. How much area (in hectares) has been used for wheat, potatoes and onions? (1 hectare = 10,000 m²).
Solution:
Let ABC be the field where wheat is grown. Also let ACD be the field which has been divided in two parts by joining C to the mid-point E of AD. In triangle ABC, we have a = 200 m, b = 240 m, c = 360 m
Therefore, s = (200 + 240 + 360)/2 m = 400 m.
∴ Area for growing wheat
= √[400(400 − 200)(400 − 240)(400 − 360)] m²
= √(400 × 200 × 160 × 40) m²
= 16000√2 m² or 1.6√2 hectares
= (16000√2)/10000 m²
= 2.26 hectares (approx.)
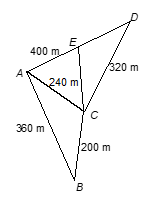
Now Ar(△AEC) = Ar(△DEC) [∵ Median divides △ into two parts of equal area]
In △ACD, We have s = (240 + 320 + 400)/2 m = 480 m.
So, area of △ACD = √[480(480 − 240)(480 − 320)(480 − 400)] m²
= √(480 × 240 × 160 × 80) m² = 38400 m² or 3.84 hectares
∴ Area for growing potatoes = Area for growing onions
= 3.84 ÷ 2 = 1.92 hectares.
Q12. Students of a school staged a rally for cleanliness campaign. They walked through the lanes in two groups. One group walked through the lanes AB, BC and CA; while the other through AC, CD and DA. Then they cleaned the area enclosed within their lanes. If AB = 9 m, BC = 40 m, CD = 15 m, DA = 28 m and ∠B = 90°, which group cleaned more area and by how much? Find the total area cleaned by the students.
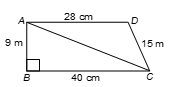
Solution:
In △ABC = 9 m and BC = 40 m, ∠B = 90°, we have
∴ AC = √(9² + 40²) m [By Pythagoras theorem]
= √(81 + 1600) m
= √1681 m = 41 m
Therefore, the first group has to clean the area of triangle ABC,
Area of △ABC = (1/2) × base × height
= (1/2) × 40 × 9 m² = 180 m²
The second group has to clean the area of triangle ACD,
Here, s = (41 + 15 + 28)/2 m = 42 m
Therefore, area of △ACD = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[42(42 − 41)(42 − 15)(42 − 28)] m²
= √(42 × 1 × 27 × 14) m² = 126 m²
So, first group cleaned 180 m², which is (180 − 126) m², i.e., 54 m² more than the area cleaned by the second group.
Total area cleaned by all the students = (180 + 126) m² = 306 m².
Q13. A rhombus has perimeter 100 m and one of its diagonal is 40 m. Find the area of the rhombus.
Solution:
ABCD is the rhombus having perimeter = 100 m and AC = 40 m.
Now, we have AB = BC = CD = AD = 25 m
∴ Ar(△ABC) = Ar(△ADC)
Sides of △ABC are 25 m, 25 m and 40 m.
∴ s = (25 + 25 + 40)/2 = 45 m.
Area of △ABC = √[45(45 − 25)(45 − 25)(45 − 40)] m²
= √(45 × 20 × 20 × 5) m²
= √(9 × 25 × 20 × 20) = 3 × 5 × 20 m²
= 300 m²
∴ Ar(△ADC) = 300 m².
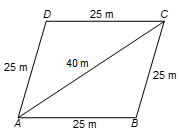
Hence, the area of the rhombus ABCD = arc (△ABC) + arc (△ADC)
= 300 m² + 300 m²
= 600 m².
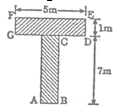
Q14. A kite in the shape of a square with a diagonal 32 cm and an isosceles triangle of base 8 cm and sides 6 cm each is to be made of three different shades as shown in figure. How much paper of each shade has been used in it?
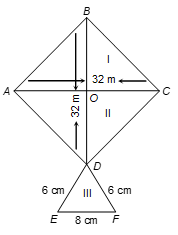
Solution:
Since diagonals of a square bisect each other at right angle.
Therefore, OA = OB = OC = OD = 16 cm
Now, Area of part I = 2 × area of △AOB
= 2 × [(1/2) × OA × OB]
= 2 × (1/2) × 16 × 16 cm²
= 256 cm²
Similarly, Area of part II = 256 cm²
In △DEF, we have s = (8 + 6 + 6)/2 = 20/2 = 10 cm
∴ Area of part III = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[10(10 − 6)(10 − 8)(10 − 6)] cm²
= √(10 × 4 × 2 × 4) cm² = √(5 × 2 × 4 × 2 × 4) cm²
= 8√5 cm² = 8 × 2.23 cm²
= 17.84 cm²
Q15. Radha made a picture of an aeroplane with coloured paper as shown in figure. Find the total area of the paper used.
Solution:
Area of part I:
Part I is enclosed by a triangle of sides a = 5 cm, b = 5 cm and c = 1 cm
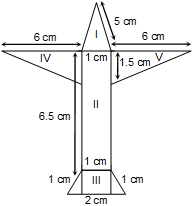
∴ s = (5 + 5 + 1)/2 = 11/2
∴ Area of part I = √[s(s − a)(s − b)(s − c)]
= √[(11/2)(11/2 − 5)(11/2 − 5)(11/2 − 1)] cm²
= √[(11/2) × (1/2) × (1/2) × (9/2)] cm²
= (3/4)√11 cm²
= (3/4) × 3.32 cm²
= 2.49 cm²
Area of part II:
Part II is a rectangle of length 6.5 cm and breadth 1 cm.
∴ Area of part II = 6.5 × 1 cm² = 6.5 cm²
Area of part III:
Part III is trapezium as shown in figure
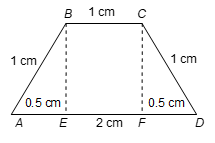
In △ABE, we have AB² = AE² + BE²
∴ (1)² = (0.5)² + (BE)²
∴ 1 = 0.25 + BE²
∴ BE = √(1 − 0.25) = √0.75 = √(3/4)
∴ Area of part III = (1/2)(AD + BC) × BE
= (1/2)(2 + 1) × (√3/4) cm² = (3√3/4) cm² = 1.3 cm²
Area of part IV:
Part IV is a right triangle whose two sides are of lengths 6 cm and 1.5 cm.
∴ Area of part IV = (1/2) × 6 × 1.5 cm² = 4.5 cm²
Area of part V:
Part-IV and part V are congruent.
∴ Area of part V = 4.5 cm²
Hence, total area of the paper used = (2.49 + 6.5 + 1.3 + 4.5 + 4.5) cm² = 19.29 cm².
Q16. A field is in the shape of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 50 m and 15 m. The non-parallel sides are 20 m and 25 m. Prove that area of the trapezium is (1300√6)/7 m².
Solution:
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD, AB = 50, CD = 15 m, BC = 25 m and AD = 20 m.
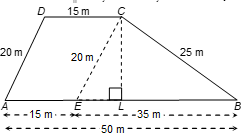
BC and AD are non-parallel sides of trapezium. Through the vertex C, we draw CE || DA and CE meeting AB at E. ABED becomes a parallelogram. Then AE = 15 m, BE = 35 m and CE = 20 m.
AE = DC = 15 m [opposite sides of ||gm]
and AD = CE = 20 m [opposite sides of ||gm]
In △CEB, s = (20 + 35 + 25)/2 = 40 m
Area of △CEB = √[40(40 − 20)(40 − 35)(40 − 25)] m²
= √(40 × 20 × 5 × 15) m² = 100√6 m² ...(i)
Now, we have CL ⊥ BE and let CL = h.
Area of △CEB = (1/2) × BE × h
= (1/2) × 35 × h m².
Thus, (1/2) × 35 × h = 100√6 [from (i)]
∴ h = (40√6)/7 m.
Area of the trapezium ABCD = (1/2)(AB + CD) × h
= (1/2)(50 + 15) × (40√6)/7 m² = (1300√6)/7 m²
Exercise 1
Ques. The area of the field ABGFEA is:
(a) 7225 m²
(b) 7230 m²
(c) 7235 m²
(d) 7240 m²
Ques. Area of shaded portion as shown in the figure:
(a) 12 m²
(b) 13 m²
(c) 14 m²
(d) 15 m²
Ques. The lengths of four sides and a diagonal of the given quadrilateral are indicated in the diagram. If a denotes the area of quadrilateral, then A is:
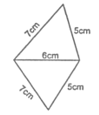
(a) 12√6
(b) √6
(c) 6√6
(d) √6'
Ques. In the sides of a triangle are doubled, then its area:
(a) Remains the same
(b) Becomes doubled
(c) Becomes three times
(d) Becomes four times
Ques. Inside a triangular garden there is a flower bed in the form of a similar triangle. Around the flower bed runs a uniform path of such a width that the side of the garden are double of the corresponding sides of the flower bed. The areas of the path and the flower bed are in the ratio:
(a) 1 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 1 : 2
(d) 3 : 1
Asnwers to Exercise 1
- A
- A
- A
- D
- D
Exercise 2
Ques. ABCD is a quadrilateral such that AB = 5 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 7 cm, AD = 6 cm and diagonal BD = 5 cm. Prove that the area of the quadrilateral ABCD is 4(3 + √6) cm².
Ques. ABCD is a quadrilateral such that AB = 26 m, BC = 27 m, CD = 7m, DA = 24 m and ∠ADC = 90°. Prove that the area of the quadrilateral is 375.72 m². (√14 = 3.74).
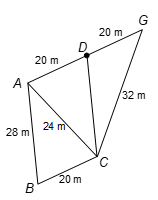
Ques. In figure, AB = 28 m, AC = 24 m, BC = 20 m, CG = 32 m, AG = 40 m and D is mid-point of AG. Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD.
Ques. A rhombus has perimeter 64 m and one of the diagonals is 22m. Prove that the area of the rhombus is 66√15 m².
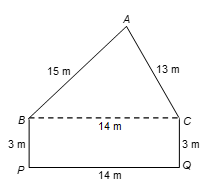
Ques. A municipal corporation wall on road side has dimensions as shown in figure. The wall is to be used for advertisements and it yields an earning of Rs. 400 per m² in a year. Find the total amount of revenue earned in a year.
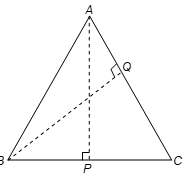
Ques. In figure, a triangular park has sides BC = 56 m, AC = 52 m and AB = 60 m. AP ⊥ BC and AQ ⊥ AC. Lamp posts are erected at the positions A, B, C, P and Q. Find the distance between A and P; and distance between B and Q.
Ques. A triangle and a parallelogram have a common side and are of equal areas. The triangle having sides 26 cm, 28 cm and 30 cm stands on the parallelogram. The common side of the triangle and the parallelogram is 28 cm. Find the vertical height of the triangle and that of the parallelogram.
Ques. A park, in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD has ∠C = 90°, AB = 10 m, BC = 8 m, CD = 6 m and AD = 6 m. prove that the area of the quadrilateral is equal to 3[8 + √91] m².
Ques. Prove that the area of the quadrilateral ABCD is 4[√3 + 2√2] m² if AB = 6 m, BC = 6 m, CD = 4 m, AD = 4 m and diagonal AC = 4 m.
Ques. Find the area of equilateral triangle whose altitude is 8 cm.
Ques. The adjacent side of a parallelogram ABCD measure 34cm and 20cm and diagonal AC measures 42cm. Find the area of the parallelogram.
Ques. Find the percentage increase in the area of triangle if each side is triple.
Answers to Exercise 2
- 3. 96(√6 + 2) m²
- 5. Rs. 50,400
- 6. 24 m; (25 × 11)/13 m
- 7. 24 cm; 12 cm
- 10. (64√3)/3 cm²
- 11. 67cm²
- 12. 800%
Exercise 3
Ques. In the given figure, △ABC is a equilateral triangle the length of whose side is equal to 10 cm and △DBC is right-angled at D and BD = 8 cm. Find the area of the shaded region. Take √3 = 1.732.
Ques. Calculate the area of the triangle whose sides are 18 cm, 24 cm and 30 cm in length. Also, find the length of the altitude corresponding to the smallest side of the triangle.
Ques. The sides of a triangle are 10 cm, 24 cm and 26 cm. Find its area and the longest altitude.
Ques. Two sides of a triangular field are 85 m and 154 m in length, and its perimeter is 324 cm. Find (i) the area of the field, and (ii) the length of the perpendicular from the opposite vertex on the side measuring 154 cm.
Ques. The sides of a triangular field are 165 cm, 143 cm and 154 cm. Find the cost of ploughing it at 12 paise per sq. m.
Ques. The base of an isosceles triangle measures 80 cm and its area is 360 cm². Find the perimeter of the triangle.
Ques. The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 42 cm and its base is 1(1/2) times each of the equal sides. Find (i) the length of each side of the triangle, (ii) the area of the triangle, and (iii) the height of the triangle.
Ques. The perimeter of a right angle triangle is 40 cm. Its hypotenuse is 17 cm. Find the sides containing the right angle. Also find the area of the triangle.
Ques. Find the area and perimeter of an isosceles right-angled triangle, each of whose equal sides measures 10 cm. Take √2 = 1.414.
Ques. The area of a square field in 8 hectares. How long would a man take to cross its diagonal by walking at the rate of 4 km per hour?
Ques. A rhombus shaped field has green for 18 cows to graze. If each side of the rhombus is 30 m and its longer diagonal is 48 m, how much area of grass field will each cow be getting?
Answers to Exercise 3
- 19.3 cm²
- 216 cm, 24 cm
- 120 cm², 24 cm
- (i) 2772 cm² (ii) 36 cm²
- Rs. 1219.68
- 162 cm
- (i) 12 cm, 12 cm, 18 cm (ii) 71.42 cm² (iii) 7.94 cm
- 8 cm, 15 cm & 60 cm²
- 50 cm², 34.14 cm
- 6 minutes
- 48 m²