About Surface Areas and Volumes – Class 9 Maths
The class-9 maths notes for the Chapter-Surface Areas and Volumes chapter connect geometry to real-world applications. Our Class 9 maths notes explain the formulas for finding surface area and volume of cubes, cuboids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. The NCERT solutions for class 9 Maths guide students through each exercise with clear explanations and solved examples.
Our Class 9 Maths tuition ensures that students can visualise 3D shapes, apply formulas correctly, and solve complex word problems with ease. With personalised guidance, students develop a strong grasp of spatial understanding and analytical thinking.
Solid Figures
If any figure such as cuboids, which has three dimensions length, width and height are known as three dimensional figures. Where are rectangle has only two dimensions i.e. length and width. Three dimensional figures have volume in addition to areas of surface from which these solid figures are formed.
Cuboid
A cuboid is a solid figure, held by six rectangular plane regions
Here, In cuboid we have six faces namely
We also have 12 edges, where two sides meets namely OA,AB,BC,OC,FG,EF,ED,OG,AF,OE,BG,CD.
Cube
A cuboid in which we have all length, breadth, height of equal lengths, is called a cube.
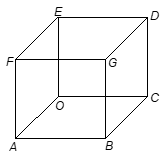
It also has six faces and twelve edges.
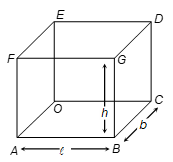
Surface Area of a Cuboid and a Cube
Total Surface Area of Cuboid
= Ar(ABCO) + Ar(EFGD) + Ar(AOEF) + Ar(BCDG) + Ar(ABGF) + Ar(OCDE)
= ℓb + ℓb + bh + bh + ℓh + ℓh
= 2(ℓb + bh + ℓh)
Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid
= 2(bh + ℓh)
Where ℓ = length of cuboid
b = breadth of cuboid
h = height of cuboid
Total Surface Area of Cube
Since cube is a cuboid in which length (ℓ) = breadth (b) = height (h) side of cube (a) i.e. ℓ = b = h = a
∴ Total surface area of cube
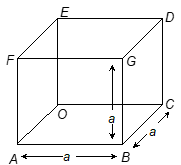
= 2(a × a + a × a + a × a)
= 2(a² + a² + a²)
Area = 2(3a²) = 6a²
Lateral Surface Area of Cube
Area = 2(a × a + a × a)
= 2(a² + a²) = 2 × 2a²
= 4a²
So, lateral surface area of cube = 4a²
Where a = length of a side.
Length of Diagonal of a Cuboid
Length of diagonal = OG = AD = BE = CF
= √(ℓ² + b² + h²)
ℓ = length; b = breadth; h = height
Length of Diagonal of a Cube
Length of diagonal = OG = AD = BE = CF
= √(a² + a² + a²)
= √(3a²) = √3a unit
Where a = length of a side.
Ex 1. Find the surface area of a chalk box whose length, breadth and height are 16 cm, 8 cm and 6 cm, respectively.
Sol. A chalk box is in the form of a cuboid.
ℓ = 16 cm, b = 8 cm and h = 6 cm
Surface area of the cuboid = 2(ℓb + bh + ℓh)
= 2(16×8 + 8×6 + 16×6) cm²
= 2(128 + 48 + 96) cm²
= 544 cm²
Ex 2. Find the surface of cube whose edge is 11 cm.
Sol. Surface area of a cube = 6 (edge)²
Here, edge = 11 cm
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6(11)² cm²
= (6 × 121) cm²
= 726 cm²
Volume of a Cube and Cuboid
Volume of cuboid = (length) × (breadth) × (height)
= ℓ × b × h
So, V = ℓbh cubic unit ...(i)
Volume of cube = a × a × a cubic unit
So, V = a³ cubic unit
Where a = side of cube
From (i), it is clear that
length = volume/(breadth × height)
breadth = volume/(length × height)
height = volume/(length × breadth)
Ex 3. A matchbox measures 4 cm × 2.5 cm × 1.5 cm. What will be the volume of a packet containing 12 such boxes?
Sol. A matchbox is in the form of a cuboid.
∴ Volume of one match box = (4 × 2.5 × 1.5) cm³ = 15 cm³ [∵ Volume = ℓ × b × h]
Hence, Volume of a packet containing 12 match boxes = 12 × 15 cm³ = 180 cm³
Ex 4. The volume of a cuboid is 440 cm³ and the area of its base is 88 cm². Find its height.
Sol. We have,
Volume = 440 cm³ and area of the base = 88 cm²
Height = Volume/Area of the base
∴ Height = 440/88 cm = 5 cm
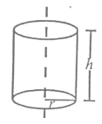
Cylinder
Curved surface area of cylinder (C.S.A.)
It is the area of surface from which the cylinder is formed. When we cut this cylinder, we will find a rectangle with length 2πr are height h units.
(i) C.S.A. of cylinder = (2πr) × h = 2πrh.
(ii) T.S.A = C.S.A. + circular top & bottom
= 2πrh + (πr²) + (πr²)
= 2πrh + 2πr²
= 2πr(h + r) sq.units
(iii) Volume of cylinder = Area of base × height
= (πr²) × h
= πr²h cubic units
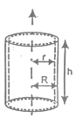
Hollow cylinder
(i) C.S.A. of hollow cylinder = 2π(R + r)h sq. units
(ii) T.S.A. of hollow cylinder = 2π(R + r)h + π(R² – r²)
= π(R + r) [2h + R - r] sq. units
(iii) Volume of hollow cylinder = π(R² – r²)h cubic units
Where, r = inner radius of cylinder
R = outer radius of cylinder
h = height of the cylinder
Ex 5. Savitri had to make a model of a cylindrical kaleidoscope for her science project. She wanted to use chart paper to make the curved surface of the kaleidoscope. What would be the area of chart paper required by her, if she wanted to make a kaleidoscope of length 25 cm with a 3.5 cm radius? (π = 22/7)
Sol. Radius of the base of the cylindrical kaleidoscope (r) = 3.5 cm.
Height (length) of kaleidoscope (h) = 25 cm.
Area of chart paper required = curved surface area of the kaleidoscope
= 2πrh
= 550 cm²
Ex 6. The curved surface area of a right circular cylinder of height 14 cm is 88 cm². Find the diameter of the base of the cylinder.
Sol. Let r be the radius and h be the height of the cylinder. Then,
2πrh = 88 and h = 88 [Given]
⇒ 2 × (22/7) × r × 14 = 88
⇒ 88r = 88
⇒ r = 1
∴ Diameter of the base = 2r = 2 cm
Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone
Curved Surface Area of a Cone
C = πrℓ
C = curved surface area
r = radius of base of cone
ℓ = slant height
ℓ = √(h² + r²)
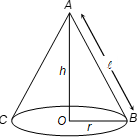
Total Surface Area of Cone
T = πrℓ + πr²
= πr(r + ℓ)
Here, T = total surface area
r = radius of base of cone
ℓ = slant height of cone
Volume of a Right Circular Cone
Volume of right circular cone
V = (1/3)πr²h
Where
V = volume of cone
r = radius of base of cone
h = height of cone
Ex 7. Find the curved surface area of a right circular cone whose slant height is 10 cm and base radius is 7 cm.
Sol. Curved surface area = πrℓ
= (22/7) × 7 × 10 cm²
= 220 cm²
Ex 8. The height of a cone is 16 cm and its base radius is 12 cm. Find the curved surface area and the total surface area of the cone (π = 3.14).
Sol. Here, h = 16 cm and r = 12 cm
So, from ℓ² = r² + h², we have
ℓ = √(16² + 12²) cm = 20 cm
Curved surface area = πrℓ
= 3.14 × 12 × 20 cm²
= 753.6 cm²
Total surface area = πℓ + πr²
= (753.6 + 3.14×12×12) cm²
= (753.6 + 452.16) cm²
= 1205.76 cm²
Sphere and Hemi Sphere
Sphere: Sphere is a three dimensional figure, which is made up of all points in the space, which lie at a constant distance called the radius, from a fixed point called the centre of sphere.
Hemi-sphere: If we exactly divide the sphere in two parts, then each part is known as hemisphere.
Surface Area of Sphere
= 4πr²
Where r = radius of sphere.
Curved Surface Area of Hemi Sphere
= 2πr²
Where r = radius of hemi-sphere.
Total Surface Area of Hemi Sphere
= 2πr² + πr²
= 3πr²
Where r = radius of hemi-sphere.
Volume of Sphere and Hemi Sphere
Volume of Sphere
= (4/3)πr³
Where r = radius of sphere
Volume of Hemi Sphere
= (2/3)πr³
Where r = radius of hemi-sphere
Ex 9. Find the surface area of a sphere of radius 7 cm.
Sol. The surface area of a sphere of radius 7 cm would be
4πr² = 4 × (22/7) × 7 × 7 cm² = 616 cm²
Ex 10. Find
(i) the curved surface area and
(ii) the total surface area of a hemisphere of radius 21 cm.
Sol. (i) Curved surface area of a hemisphere of radius 21 cm would be
= 2πr² = 2 × (22/7) × 21 × 21 cm² = 2772 cm²
(ii) Total surface area of the hemisphere would be
3πr² = 3 × (22/7) × 21 × 21 cm² = 4158 cm²
Exercise – 1
Ques 1. The height of a conical tent at the centre is 5m. The distance of any point on its circular base from the top of the tent is 13m. The area of the slant surface is :
(a) 144 π sq m
(b) 130 π sq m
(c) 156 π sq m
(d) 169 π sq m
Ques 2. A rectangular sheet of paper 22 m long and 12 cm broad can be curved to form the lateral surface of a right circular cylinder in two ways. Taking π = 22/7, the difference between the volumes of the two cylinders thus formed is :
(a) 200 c.c.
(b) 210 c.c.
(c) 250 c.c.
(d) 252 c.c.
Ques 3. The percentage increase in the surface area of a cube when each side is increased to 3/2 times the original length is
(a) 225
(b) 200
(c) 175
(d) 125
Ques 4. A cord in the form of a square enclose the area 'S' cm². if the same cord is bent into the form of a circle, then the area of the circle is
(a) πS²/4
(b) 4πS²
(c) S/4π
(d) 4S/π
Ques 5. If 'I', 'b' and 'h' if a cuboids are increased, decreased and increased by 1%, 3% and 2% respectively, then the volume of the cuboids
(a) increase
(b) decrease
(c) increase or decreases depending on original dimensions
(d) can't be calculated with given data
Ques 6. The radius and height of a cone are each increased by 20%, then the volume of the cone is increased by
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 60%
(d) 72.8%
Ques 7. There is a cylinder circumscribing the hemisphere such that their bases are common. The ratio of their volume is
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 3 : 4
Ques 8. Consider a hollow cylinder of inner radius r and thickness of wall t and length ℓ. The volume of the above cylinder is given by
(a) 2πℓ(r² - ℓ²)
(b) 2πℓt(t/2r + 1)
(c) 2πℓ(r² + t²)
(d) 2πrℓ(r + t)
Ques 9. A cone and a cylinder have the same base area. They also have the same curved surface area. If the height of the cylinder is 3m, then the slant height of the cone (in m) is
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 7
Ques 10. A sphere of radius 3 cm is dropped into a cylindrical vessel of radius 4 cm. If the sphere is submerged completely, then the height (in cm) to which the water rises, is
(a) 2.35
(b) 2.30
(c) 2.25
(d) 2.15
Ques 11. The dimensions of a cuboid are 8 cm × 6 cm × 5 cm. Its total surface area will be
(a) 256 cm²
(b) 236 cm²
(c) 224 cm²
(d) none of these
Ques 12. A right circular cone have diameter 8 cm and slant height is 5 cm. The volume of the cone is
(a) 14π cm³
(b) 18π cm³
(c) 16π cm³
(d) none of these
Ques 13. A cylindrical vessel having radius and depth 7 cm and 30 cm respectively. Litres of milk contained by vessel is
(a) 4.42 ℓ
(b) 4.62 ℓ
(c) 5.42 ℓ
(d) none of these
Ques 14. A wooden sphere has radius 3.5 cm. The density of wood is 0.9 g per cm³. The mass of the wooden sphere is
(a) 161.7 g
(b) 150 g
(c) 158.3 g
(d) 172.3 g
Ques 15. A hemispherical bowl has radius of 2.1 cm. Capacity of 20 such bowls will be
(a) 388 cm³
(b) 430 cm³
(c) 360 cm³
(d) 424 cm³
Ques 16. Volume of a sphere whose surface area is 154 cm² will be
(a) 279(2/3) cm³
(b) 79(2/3) cm³
(c) 379(2/3) cm³
(d) 179(2/3) cm³
Ques 17. Volume of largest cone that can be fit in a cube whose edge is 14 cm will be
(a) 618.6 cm³
(b) 718.6 cm³
(c) 518.6 cm³
(d) 818.6 cm³
Ques 18. A conical pit having diameter 3.5 m is 12 m deep. Capacity of pit in kiloliters is
(a) 38.5 kl
(b) 39.5 kl
(c) 37.5 kl
(d) none of these
Ques 19. Diameter of a sphere is decreased by 25%. Percentage decrease in its curved surface area will be
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 60%
(d) 43.5%
Ques 20. Number of 3 meters cubes that can be cut from a cuboid measuring 18 m × 12 m × 9 m will be
(a) 72
(b) 62
(c) 52
(d) none of these
Answers to Exercise 1
1. (c)
2. (b)
3. (d)
4. (d)
5. (b)
6. (d)
7. (c)
8. (b)
9. (c)
10. (c)
11. (b)
12. (d)
13. (b)
14. (a)
15. (a)
16. (d)
17. (b)
18. (a)
19. (d)
20. (a)
Exercise 2
Ques 1. Find the curved surface area of a right circular cone whose slant height is 14 cm and base radius is 10 cm. (Take π = 22/7)
Ques 2. The length, breadth and height of a room are 5 m, 4 m and 3 m respectively. Find the cost of white washing the walls of the room and the ceiling at the rate of Rs. 7.50 per m².
Ques 3. The inner diameter of a cylindrical wooden pipe is 24 cm and its outer diameter is 28 cm. The length of the pipe is 35 cm. Find the mass of the pipe, if 1 cm³ of wood has a mass of 0.6 g.
Ques 4. It costs Rs. 2200 to paint the inner curved surface of a cylindrical vessel 10 m deep. If the cost of painting is at the rate of Rs. 20 per m², find
(i) inner curved surface area of the vessel,
(ii) radius of the base,
(iii) capacity of the vessel.
Ques 5. Gopal sweets placed an order for making 30 cm x 20 cm x 6 cm cardboard boxes for packing their sweets. For all the overlaps, 4% of the total area is required extra. If the cost of the cardboard is 25 paisa for 100 cm², find the cost of the cardboard used for making 1000 boxes.
Ques 6. 1 cm thick metal sheet is used to make a cylindrical container which is open at the top. The outer diameter is 30 cm and the outer height is 84 cm. Find the
(i) inner curved surface area
(ii) outer curved surface area. (Take π = 22/7)
Ques 7. The diameter of a road roller is 140 cm and its length is 2.2 m. It takes 400 complete revolutions to move once over to level a stretch of road 2.2 m wide. Find the surface area of the stretch of road leveled in m². (Take π = 22/7)
Ques 8. An open metallic conical tank is 4 m deep and its top diameter is 6 m (as shown in figure). Find
(i) the area of the metallic sheet required to make the tank.
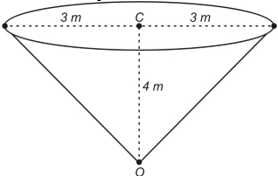
(ii) the cost of painting the outer surface at the rate of Rs. 8 per m². (Take π = 3.14)
Ques 9. Along a high way 50 conical pillars constructed. Each pillar has base diameter 28 cm and vertical height 48 cm. Find the total cost of painting these pillars at the rate of Rs. 120 per m².
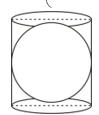
Ques 10. A right circular cylinder just encloses a sphere (figure). If the height of the cylinder is 21 cm, then find the surface area of the cylinder. (Take π = 22/7)
Ques 11. The capacity of a cuboidal water reservoir is 450000 litres of water. Find the length of the reservoir if its breadth and height are respectively 5 m and 3 m.
Ques 12. A river 3.5 m deep and 28 m wide is flowing at the rate of 2.4 km per hour. How many litres of water will flow into the sea in 10 minutes? (1 m³ = 1000 litres of water)
Ques 13. The capacity of a closed cylindrical vessel of height 84 cm is 26.4 litres. How many square metres of metal is required to make seven such vessels?
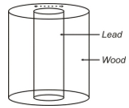
Ques 14. In figure, a cylindrical groove is made in a cylindrical 21 cm long solid piece of wood. The grove is filled with lead and this cylindrical lead block is of same length as that of the wooden cylindrical piece. If the diameter of the lead cylinder is 3 cm and the outer diameter of the wooden cylinder is 12 cm, find the volume of the wood and that of the lead.
Ques 15. If h, c, V are respectively the height, the curved surface and the volume of a cone, prove that 3πVh³ – c²h² + 9V² = 0.
Ques 16. A hemispherical dome is constructed on a building at the rate of Rs. 18 per m² of the outer curved surface area. The cost of construction of the dome is Rs. 1386. Find the volume of space occupied by the dome. (Take π = 22/7).
Ques 17. Sixty four solid metallic spheres, each of radius 0.15 cm are melted to form a single bigger sphere. Find the radius of the bigger sphere.
Ques 18. Each edge of a cube is increased by 50%. Find the percentage increase in the surface area of the cube.
Ques 19. A closed iron tank 12 m long, 9 m wide and 4 m deep is to be made. Determine the cost of iron sheet used at the rate of Rs. 5 per metre sheet, sheet being 2 m wide.
Ques 20. A cuboid has total surface area of 40 m² and its lateral surface area is 26 m². Find the area of its base.
Ques 21. Length of a class-room is two times its height and its breadth is 1½ times its height. The cost of white-washing the walls at the rate of Rs. 1.60 per m² is Rs. 179.20. Find the cost of tiling the floor at the rate of Rs. 6.75 per m².
Ques 22. A conical pit of top diameter 3.5 m is 12 m deep. What is its capacity in kilolitres?
ANSWERS TO EXERCISE – 2
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. | 440 cm² |
| 2. | Rs 555 |
| 3. | 3.432 kg. |
| 4. | (i) 110 m² (ii) 1.75 m. (iii) 96.25 kl. |
| 5. | Rs 4680 |
| 6. | (i) 7304 cm² (ii) 7920 cm² |
| 7. | 3872 m² |
| 8. | (i) 47.1 m² (ii) Rs 376.80 |
| 9. | Rs 1320 |
| 10. | 1386 cm² |
| 11. | 30 m |
| 12. | 39200000 litres |
| 13. | 41.36 m² |
| 14. | 2227.5 cm³, 148.5 cm³ |
| 16. | 89(5/6) m³ |
| 17. | 0.6 cm |
| 18. | 125% |
| 19. | Rs 960 |
| 20. | 7 m² |
| 21. | Rs 324 |
| 22. | 38.5 kilo litres |