Tired of Confusing Chemistry Notes? Master Surface Chemistry & Ace Your CBSE Exams!
Stop struggling with dense textbooks. Finally understand the core concepts of Surface Chemistry with our crystal-clear, exam-focused notes. Get the confidence you need to score top marks!
Why Our Surface Chemistry Notes Are a Game-Changer
We break down every complex topic into simple, digestible points. Our notes are designed to help you learn faster and retain more, ensuring you're fully prepared for your exams.
-
Clear Up All Confusion: Instantly grasp the difference between adsorption and absorption with easy-to-understand definitions and examples.
-
Master Adsorption Types: Get a side-by-side comparison of Physical Adsorption and Chemisorption, covering everything from van der Waal's forces to activation energy.
-
Visualize Complex Theories: Understand Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherms with clearly labeled graphs and simplified equations.
Unlock the Secrets of Catalysis: Learn how catalysts work, including homogeneous, heterogeneous, and enzyme catalysis, and how they lower activation energy to speed up reactions.
-
Conquer Colloids: Dive deep into the world of colloids, from sols and gels to emulsions. Easily learn their properties like the Tyndall effect and electrophoresis.
-
Real-World Applications: Connect theory to practice by learning about the real-world applications of colloids in medicines, sewage disposal, and delta formation.
What's Inside? A Complete CBSE Curriculum Breakdown
Our notes cover every essential topic you need for your exams.
1. Adsorption
-
Fundamentals: Definitions of adsorbate, adsorbent, desorption, and occlusion8.
-
Types of Adsorption: A detailed comparison of physical adsorption (physisorption) and chemical adsorption (chemisorption).
-
Factors Affecting Adsorption: In-depth analysis of surface area, nature of the gas, temperature, and pressure.
-
Adsorption Isotherms: Clear explanations of Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms11111111.
2. Catalysis
-
Introduction: Positive and negative catalysts12.
-
Types of Catalysis: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous catalysis with examples like the Contact process and Haber's process.
-
Enzyme Catalysis: The "lock and key" model and the high specificity of enzymes.
3. Colloids
-
Classification: Types of colloids based on the physical state (sols, gels, aerosols) and nature of interaction (lyophilic and lyophobic).
-
Colloidal Systems: Multimolecular, macromolecular, and associated colloids (micelles).
-
Properties & Purification: Key properties like the Tyndall effect and coagulation, plus purification methods like dialysis and ultra-filtration.
-
Emulsions: Oil in water vs. water in oil types and the process of emulsification.
"Surface Chemistry always seemed so abstract. The concepts of micelles and isotherms were really confusing. These notes, especially with the clear diagrams and comparison tables, made all the difference. I finally feel ready for my board exams!"
- Aashi S., Class 12 Student
Ready to Boost Your Chemistry Score?
Don't wait until it's too late. Get the best notes for Surface Chemistry and turn a difficult chapter into one of your strongest. Fill out the form below to receive a free sample and get more details!
Surface chemistry is the branch of chemistry, which deals with the study of phenomena occurring at the surface separating the two bulk phases. These two bulk phases can be pure compounds or solutions.
ADSORPTION
The phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of the substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid resulting into a higher concentration of molecules on the surface is called adsorption. The substance thus adsorbed on the surface is called the adsorbate and the substance on which it is adsorbed is called adsorbent. The reverse process, i.e. removal of the adsorbed substance from the surface is called desorption (which can be brought about by heating or reducing the pressure).
The adsorption of gases on the surface of metals is called occlusion.
Difference between adsorption and absorption:
|
Adsorption |
Absorption |
|
It is a surface phenomenon, i.e. it occurs only at the surface of the adsorbent. |
It is a bulk phenomenon, i.e. occurs throughout the body of the material. |
|
In this phenomenon the concentration on the surface of adsorbent is different from that in the bulk. |
In this phenomenon, the concentration is same throughout the material. |
Types of Adsorption
There are two main types of adsorption.
(i) Physical adsorption
(ii) Chemisorption
Physical Adsorption & Chemical Adsorption
Difference between physical adsorption and chemisorption:
|
Physical Adsorption |
Chemisorption |
||
|
1. |
The forces operating in these cases are weak van der Waal’s forces. |
1. |
The forces operating in these cases are similar to those of a chemical bond. |
|
2. |
The heats of adsorption are low, i.e. about 20-40 kJmol-1. |
2. |
The heats of adsorption are high, i.e. about 40 – 400 kJmol-1 |
|
3. |
The process is reversible, i.e. desporption of the gas occurs by increasing the temperature or decreasing the pressure. |
3. |
The process is irreversible. |
|
4. |
It does not require any activation energy. |
4. |
It requires activation energy. |
|
5. |
This types of adsorption usually takes place at low temperature and decreases with increases of temperature. |
5. |
This type of adsorption first increases with increase of temperature. The effect is called activated adsorption. |
|
6. |
The amount of the gas absorbed is related to the ease of liquification of the gas. |
6. |
There is no such correlation. |
|
7. |
It forms multimolecular layer. |
7. |
It forms unimolecular layer. |
Factors Affecting the Adsorption of Gases
Almost all solids adsorb gases to some extent, however, the exact amount of a gas adsorbed depends upon the following factors.
(i) Nature and surface area of the adsorbent: The greater the surface area of the adsorbent, greater is the volume of the gas adsorbed. Therefore, charcoal and silica gel are excellent adsorbents because they have highly porous structures and hence large surface areas.
(ii) Nature of the gas: Different gases are adsorbed to different extents by the same adsorbent at the same temperature. As critical temperature increases, ease of liquefaction increases and hence adsorption increases.
(iii) Effect of temperature: Adsorption is generally temperature dependent. Mostly, adsorption is an exothermic process and therefore, adsorption decreases with increasing temperature. However, as expected for endothermic adsorption processes, adsorption increase with increase in temperature.
(iv) Pressure: At constant temperature, the adsorption of a gas increases with increase of pressure. It is observed that at low temperature, the adsorption of a gas increases very rapidly as the pressure is increased.
(v) Activation of the solid adsorbent: This is usually done by increasing the surface area of the adsorbent by any of the following ways,
(a) making the surface of the adsorbent rough.
(b) subdividing the adsorbent into smaller piece or grains.
(c) removing the gases already absorbed.
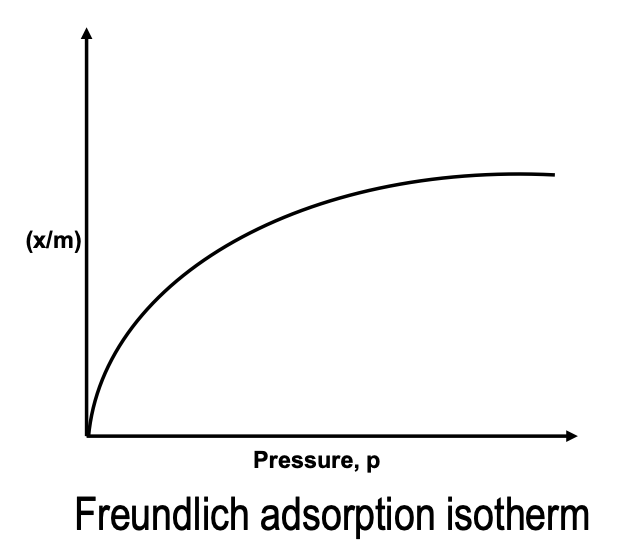
Freundlich’s Adsorption Isotherm
In case of adsorption of gases on solids, the relation between x/m and the pressure p of the gas at constant temperature is given by the equation.
x/m = Kp1/n (n > 1) .. (i)
where K and n are the parameter of the equation depending upon the nature of the gas and the solid. According to this, x/m increases with increase of p but since n > 1, x/m does not increase as rapidly as p, as can be seen from the isotherm.
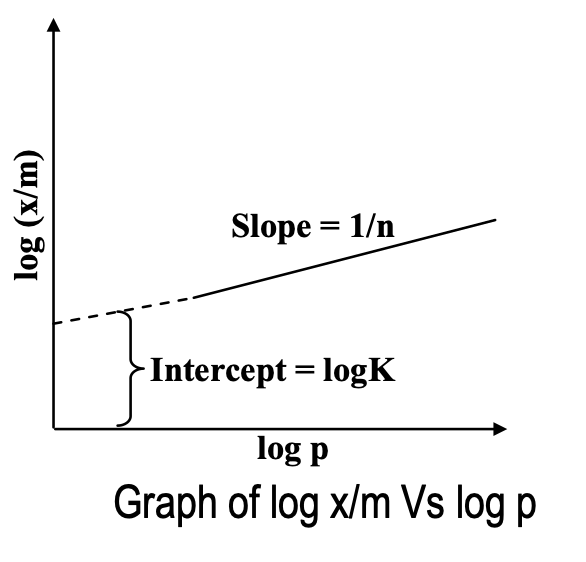
Taking logarithms on both sides of equation (i) we get,
log x/m = log K + 1/n log p ... (ii)
Thus, if we plot a graph between log(x/m) and log p, a straight line is obtained. The slope of the line is equal to 1/n and the intercept on log (x/m) axis will correspond to logK. Therefore, value of K and n can be found out
Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
One of the drawbacks of the Freundlich adsorption isotherm is that it fails at high pressure. Langmuir’s adsorption isotherm is based on kinetic theory of gases. Langmuir considered adsorption to consist of the following two opposing processes:
(i) adsorption of the gas molecules on the surface of the solid.
(ii) desorption of the adsorbed molecules from the surface of the solid.
Langmuir believed that eventually a dynamic equilibrium is established between the above two opposing processes. He also assumed that the layer of the adsorbed gas was
unimolecular. Such type of adsorption is obtained in the case of chemisorption, hence isotherm works particularly well for chemisorption.
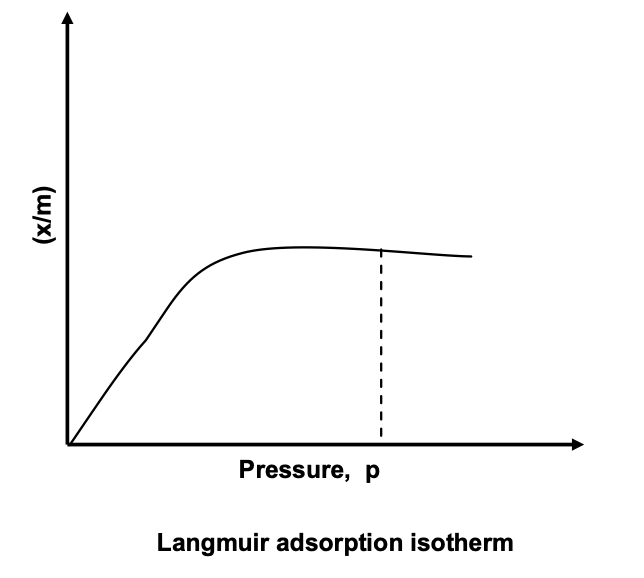
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is represented by the relation,
x/m = ap/1+bp ...(iii)
Where a and b are two Langmuir parameters. At very high pressure, the above isotherm acquires the limiting from,
At very low pressure, equation (iii) is reduced to x/m = ap
(at very low pressure) bp < < 1 …(iv b)
In order to determine the parameters a and b, equation (iii) may be written in its inverse form.
m/x = 1+bp / ap = b/a + 1/ap
A plot of m/x against 1/p gives a straight line with slope and intercept equal to 1/a and b/a, respectively, thus both parameters can be determined.
Langmuir isotherm indicates that at low pressure x/m increases linearly with p. At high pressure, x/m becomes constant, i.e. the surface is fully covered and change in pressure has no effect and no further adsorption takes place, as is evident from figure.
CATALYSIS
Catalyst is a substance which can change the speed of a chemical reaction without being used up in that reaction and the phenomenon is known as catalysis. If a catalyst increases speed of a reaction, it is called a positive catalyst and the phenomenon is called positive catalysis. While if a catalyst decreases the speed of a reaction, it is called a negative catalyst and the phenomenon is called negative catalysis. For example, oxidation of SO2 to SO3 in presence of NO (lead chamber process) or in presence of V2O5 (contact process) are examples of positive catalysis, decomposition of H2O2 in presence of phosphoric acid and oxidation of chloroform in presence of alcohol are examples of negative catalysis.
A catalyst lowers the activation energy for the forward reaction as well as for the backward reaction. As a result, the reaction follows an alternate path and the rate of forward reaction as well as that of the backward reaction are accelerated to the same extent. Hence, equilibrium constant of the reaction remains unaffected. Similarly, it may be noted that the enthalpy change of the reaction also remains unaffected. In the presence of catalyst, the equilibrium is however attained quickly.
Types of Catalysis
Catalysis can be broadly classified into two types.
1. Homogeneous catalysis:
If the catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants, it is called a homogeneous catalyst and this type of catalysis is called homogeneous catalysis. Two common examples of homogeneous catalysis are:
(i) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide in presence of nitric oxide as catalyst (in lead chamber process for manufacture of H2SO4).
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) →[NO(g)] 2SO3 (g)
Here, all substances are present in the gaseous phase. Similarly, oxidation of CO by O2 takes place in presence of NO as catalyst.
2CO (g) + O2 (g) →[NO] 2CO2 (g)
(ii) Decomposition of ozone in presence of Cl atoms acting as catalyst.
O3 + O →[Cl] 2O2
2. Heterogeneous catalysis:
If the catalyst is present in a different phase than that of the reactant, it is called a heterogeneous catalyst and this type of catalysis is called heterogeneous catalysis.
The catalyst in heterogeneous catalysis is generally solid and the reactants are mostly gases and sometimes liquids. In heterogeneous catalysis, the reaction starts at the surface of the solid catalyst that is why it is known as surface catalysis.
Some examples of heterogeneous catalysis are,
(i) Manufacture of ammonia from N2 and H2 by Haber’s process using iron as catalyst.
(ii) Synthesis of methyl alcohol (CH3OH) from CO and H2 using a mixture of Cu, ZnO and Cr2O3 as catalyst.
(iii) Manufacture of sulphuric acid by the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 using V2O5 as catalyst.
Important Features of Solid Catalysts
(i) Activity:
Activity of the catalyst is its capacity to increase the speed of the chemical reaction. It may be increased upto 1010 times.
Combination of H2 and O2 in the presence of platinum (catalyst) to form water with explosive violence is an example of catalytic activity.
In the absence of the catalyst, platinum, H2 and O2 do not combine and can be stored as such for an indefinite period.
Reaction:
2H2 + O2 —Pt→ 2H2O
The activity depends upon the extent of chemisorption. The adsorption should be reasonably strong but not so strong that the absorbed molecules become immobile and no space is available for other reactants to get adsorbed.
(ii) Selectivity:
By selectivity of a catalyst we mean its ability to direct the reaction to form particular products excluding others. For example, CO and H2 react to form different products in presence of different catalysts as follows:
CO(g) + H2(g) —Cu→ HCHO(g) CO(g) + 2H2(g) —Cu/ZnO-Cr2O3→ CH3OH(g) CO(g) + 3H2(g) —Ni→ CH4(g) + H2O(g)
Action of a catalyst is highly selective in nature, i.e. a given substance can act as a catalyst only in a particular reaction and not for all the reactions.
(iii) Shape selective catalysis by zeolites:
The catalytic reaction that depends upon the pore structure of the catalyst and the size of the reactant and product molecules is called shape selective catalysis. Zeolites are good shape selective catalysts because of their honeycomb-like structures. The reactions taking place in zeolites depend upon the size and shape of reactant and product molecule as well as upon the pores and cavities of the zeolites. That is why these types of reactions are called shape selective catalysis reactions. An important zeolite catalyst used in petroleum industry is ZSM -5. It converts alcohol directly into gasoline (petrol) by dehydration and a mixture of hydrocarbons is formed.
Enzyme catalysis:
All biological reactions are catalysed by special catalysts called enzymes. Enzymes are proteins with high molar mass. They increase rates by 108 to 1020 times. Enzymes are also extremely specific. Each reaction is generally catalysed by a particular enzyme. Urease for example, catalyses only the hydrolysis of urea and none of the several thousand other enzymes present in the cell catalyses that reaction.
(i) Activity:
Activity of the catalyst is its capacity to increase the speed of the chemical reaction. It may be increased upto 1010 times.
Combination of H2 and O2 in the presence of platinum (catalyst) to form water with explosive violence is an example of catalytic activity.
In the absence of the catalyst, platinum, H2 and O2 do not combine and can be stored as such for an indefinite period.
Reaction:
2H2 + O2 —Pt→ 2H2O
The activity depends upon the extent of chemisorption. The adsorption should be reasonably strong but not so strong that the absorbed molecules become immobile and no space is available for other reactants to get adsorbed.
(ii) Selectivity:
By selectivity of a catalyst we mean its ability to direct the reaction to form particular products excluding others. For example, CO and H2 react to form different products in presence of different catalysts as follows:
CO(g) + H2(g) —Cu→ HCHO(g) CO(g) + 2H2(g) —Cu/ZnO-Cr2O3→ CH3OH(g) CO(g) + 3H2(g) —Ni→ CH4(g) + H2O(g)
Action of a catalyst is highly selective in nature, i.e. a given substance can act as a catalyst only in a particular reaction and not for all the reactions.
Mechanism of Enzyme Action
The two most accepted mechanisms are given below.
(i) Lock and key model
The specificity of the enzymes is due to the presence of some specific regions, called the active sites which are associated with some functional groups, which form weak bond such as H-bonds, van der Waal’s attraction, with the substrate (reactant) molecules. The shape of the active site of any given enzyme is such that only a specific substrate can fit into it, in the same way as one key can open a particular lock.
Once the proper orientation has been achieved, substrate molecules react to form the products in two steps as shown in the figure.
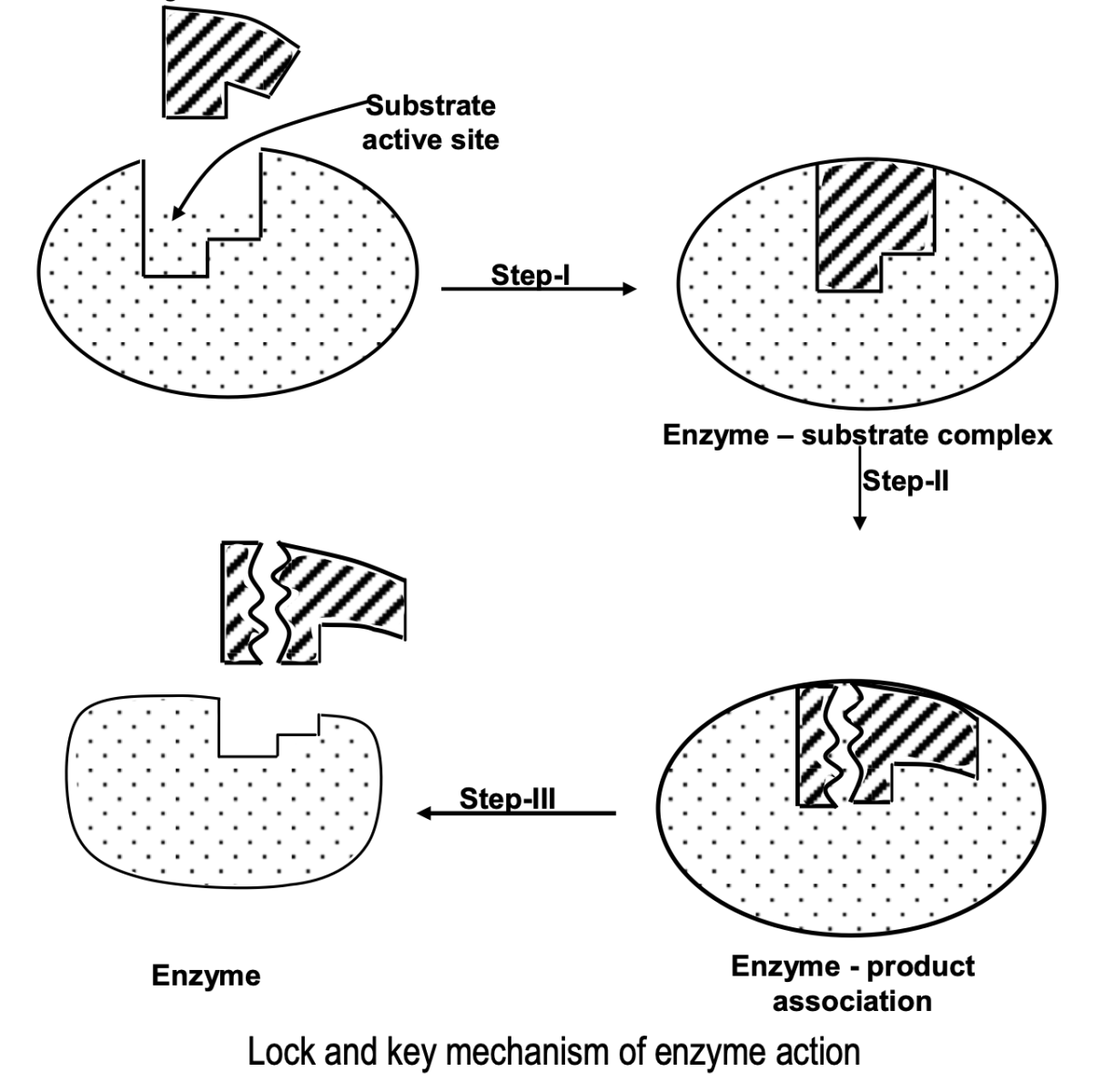
(ii) Induced fit model: According to this model, the enzyme can change its shape when the substrate comes in contact with the active site so that there is a perfect fit rather than rigidly shaped lock and key.
Example: In homogeneous catalytic reactions, the rate of reaction
(A) depends upon the concentration of catalyst
(B) independent of the concentration
(C) dependent upon the free energy change
(D) depends upon physical state of the catalyst
Solution: (A).
Catalyst forms an intermediate with reactant and thus, rate of reaction for intermediate formation depends upon concentration of catalyst.
Ex.: Enzymes catalysts are
(A) highly specific in nature
(B) non-specific
(C) solids
(D) always liquid
Solution: (A).
One enzyme catalyses only one reaction. This is highly specific action of enzyme. Sucrose (C12H22O11) is hydrolysed by invertase whereas, another sugar maltose (C12H22O11) is hydrolysed by maltase.
COLLOIDS
Between the extremes of suspensions and solutions, is a large group of systems called colloidal dispersion or simply colloids. A colloidal solution is a heterogeneous system in which one substance is dispersed (dispersed phase) as very fine particles in another substance called dispersion medium. The essential difference between a solution and a colloid is of particle size.
In a solution, the particles are ions or small molecules.
In a colloid, the dispersed phase may consist of particles of a simple marcromolecule (such as protein or synthetic polymer) or an aggregate of many atoms, ions or molecules. Colloidal particles are larger than simple molecules but small enough to remain suspended. They have a range of a diameter between 1 and 1000 nm (10-9 to 10-6 m).
Classification of Colloids
Colloids are classified on the basis of the following criterias,
(a) physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
(b) nature of interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
(c) types of particles of the dispersed phase.
- Classification based on physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium:
Depending upon whether the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are solids, liquids or gases, eight types of colloidal systems are possible. The examples of various colloids along with their typical names are listed below.
Types of colloidal systems
|
Dispersed phase |
Dispersion medium |
Type of colloid |
Example |
|
Solid |
Solid |
Solid sol |
Some coloured glasses and stones |
|
Solid |
Liquid |
Sol |
Paint, cell fluids |
|
Solid |
Gas |
Aerosol |
Smoke, dust |
|
Liquid |
Solid |
Gel |
Ghee, butter |
|
Liquid |
Solid |
Aerosol |
Fog, mist, cloud, insecticide sprays |
|
Gas |
Solid |
Solid sol |
Pumice stone, foam rubber |
|
Gas |
Liquid |
Foam |
Froth whipped cream, soap lather. |
Out of various types of colloids given above, the most common are sols (solid in liquids), gels (liquids in solids) and emulsions (liquid in liquids). Further, it may be mentioned that depending upon the dispersion medium, the sols are given special names as follows:
|
Dispersion medium |
Name of the sol |
|
Water |
Aquasol or hydrosol |
|
Benzene |
Benzosol |
|
Gases |
Aerosol |
- Based on the nature of interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium:
On this basis, colloidal sols are divided into two categories namely, lyophilic and lyophobic. If water is the dispersion medium, the terms are hydrophilic and hydrophobic.
(i) Lyophilic colloids: The word ‘lyophilic’ means liquid loving. Colloidal sols directly formed by substances like gum, gelatine, starch, rubber etc., on mixing with a suitable liquid (the dispersion medium) are called lyophilic sols. If the dispersion medium is separated from the dispersed phase (by evaporation), the sol can be reconstituted by simply remixing with the dispersion medium. That is why these sols are also called reversible sols.
(ii) Lyophobic colloids: The word ‘lyophobic’ means liquid hating substances. When substances are simply mixed with the dispersion medium they do not form the colloidal sol. These sols are readily precipitated (or coagulated) on the addition of small amounts of electrolytes, by heating or by shaking and hence are not stable. Further, once precipitated, they do not give back the colloidal sol by simple addition of the dispersion medium. Hence these sols need stabilizing agents for their preservation.
Important Properties of Colloidal Sols
(i) Colligative properties: Colloidal sols show the colligative properties, viz., relative lowering of vapour pressure, elevation in boiling point, depression in freezing point and osmotic pressure.
(ii) Optical properties-Tyndall effect: If a strong beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol placed in a dark place, the path of the beam gets illuminated. This phenomenon is called tyndall effect.
True solutions do not exhibit tyndall effect because the particles in them are too small in size and do not cause any scattering.
(iii) Electrical properties (Electrophoresis): The particles of the colloids are electrically charged and carry positive or negative charge. The dispersion medium has an equal and opposite charge making the system neutral as a whole due to similar nature of the charge carried by the particles. They repel each other and do not combine to form bigger particles. That is why a sol is stable and particles do not settle down. Arsenious sulphide, gold silver and platinum particles in their respective colloidal sols are negatively charged while particles of ferric hydroxide, aluminium hydroxide are positively charged. The existence of the electric charge is shown by the phenomenon of electrophoresis. It involves the movement of colloidal particles either towards the cathode or anode, under the influence of the electric field.
(iv) Coagulation of colloids: The presence of small amounts of appropriate electrolytes is necessary for the stability of the colloids. However, when an electrolyte is added in larger concentration, the particles of the sol take up the ions, which are oppositely charged and thus get neutralized. The neutral particles then start aggregating giving particles of larger size, which are then precipitated. This process of aggregation of colloidal particles into an insoluble precipitate by the addition of some suitable electrolyte is known as coagulation.
At lower concentration of electrolytes, the aggregation of particles is called flocculation.
The minimum amount of an electrolyte (in milli moles) that must be added to one litre of a colloidal solution so as to cause its compete coagulation is called the precipitation or coagulation value of the electrolyte.
Purification of Colloidal Sols
The colloidal sols obtained by various methods are impure and contain impurities of electrolytes and other soluble substances. These impurities may destabilize the sol. Hence, they have to be removed. A very important method of removal of soluble impurities from sols by a semipermeable membrane is known as dialysis.
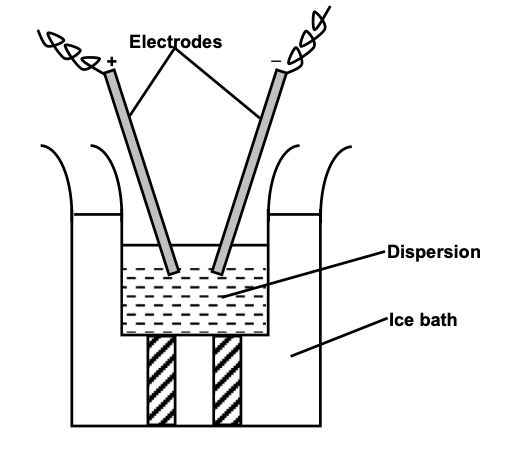
(i) Dialysis: Particles of true solutions can pass through parchment paper or cellophone membrane sol particles cannot pass through these membranes. A bag made up of such a membrane is filled with the colloidal solution and is then suspended in fresh water. The electrolyte particles pass out leaving behind the colloidal sol.
Movement of ions across the membrane can be expendited by applying electric potential through two electrodes. This method is faster than simple dialysis and is known as electrodialysis.
(ii) Ultra–filtration: In this method, colloidal sols are purified by carrying out filtration through special type of graded filters called ultra–filter. These filter papers allow only the electrolytes to pass through. These filter papers are made of particular pore size by impregnating ordinary filter paper with colloidal particles. In order to accelerate the filtration through such filter papers, increased pressure or section is employed.
(iii) Ultra-centrifugation: In this method, the colloid sol is taken in a tube which is placed in an ultra–centrifuge. On rotation of the tube at high speeds, the colloidal particles settle down at the bottom of the tube and the impurities remain in the solution called the centrifugate. The settled colloidal particles are mixed with an appropriate dispersing medium to regenerate the sol.
Preparation of Colloidal Sols
For the preparation of lyophobic and lyophilic sols different methods are employed.
(A) Preparation of lyophobic sols:
Lyophobic sols can be prepared by two types of methods.
(i) Condensation methods:
In these methods, particles of atomic or molecular size are induced to combine to form aggregates having colloidal dimensions. For this purpose, chemical as well as physical methods can be applied.
(a) Chemical methods: Colloidal solutions can be prepared by chemical reactions leading to formation of molecules by double decomposition, oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis. These molecules then aggregate leading to formation of soils.
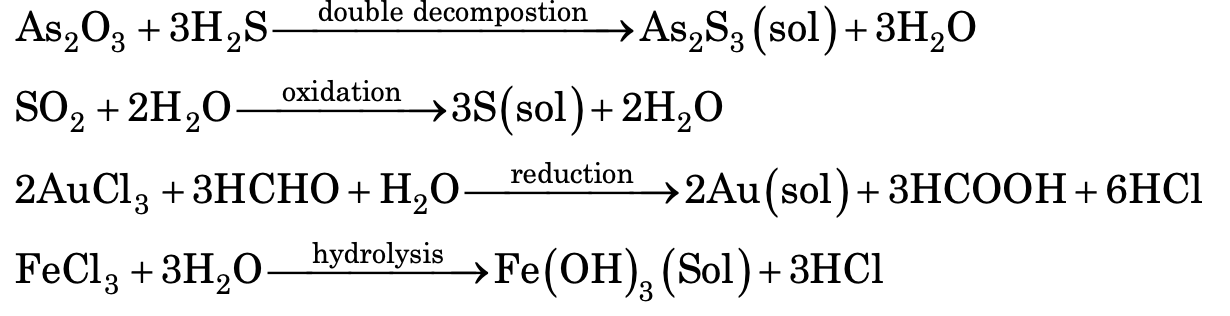
(b) Physical methods:
(I) Exchange of solvent: When a true solution is mixed with an excess of the othersolvent in which the solute is insoluble but solvent is miscible a colloids sol is obtained. For example, when a solution of sulphur in alcohol is poured in excess of water, a colloidal sol of sulphur is obtained.
(II) Excessive cooling: The colloidal sol of ice in an organic solvent such as CHCl3 or ether can be obtained by freezing a solution of water in the solvent. The molecules of water which can no longer be held in solution separately combine to form particles of colloidal size.
(ii) Dispersion methods:
In these methods, large particles of the substance are broken into particles of colloidal dimensions in the presence of dispersion medium. These are stabilized by adding some suitable stabilizer. Some of the methods employed for carrying out dispersion are given below:
(a) Mechanical dispersion: In this method, the coarse suspension of the substance is brought into a colloidal state in the dispersion medium by grinding it in a colloid mill, ball mill or ultrasonic disintegrator. The colloid mill consists of two metal discs, close together, rotating at high speed (7000 revolutions per minute) in opposite directions. The suspension particles are changed into the colloidal size.
(b) Electrical disintegration or Bredig’s arc methods:
This process involves dispersion as well as condensation. Collodial sols of metals such as gold, silver, platinum etc., can be prepared by this method. In this method, electric arc is struck between electrodes of the metal immersed in the dispersion medium. The intense heat produced vapourizes the metal, which then condenses to form particles of colloidal size.
(c) Peptization: Peptization may be defined as the process of converting a precipitate into colloidal sol by shaking it with dispersion medium in the presence of a small amount of electrolyte. The electrolyte used for this purpose is called peptizing agent. This method is applied, generally, to convert a freshly prepared precipitate into a colloidal sol.
For example, when freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 is shaken with aqueous solution of FeCl3(peptizing agent) it adsorbs Fe3+ ions and thereby breaks up into small – sized particles.
(B) Preparation of lyophilic sols:
Lyophilic sols are quite stable and can be easily prepared by shaking the lyophilic material with dispersion medium. Some examples of colloidal sols are gelatin, gum, starch, egg etc.
MACROMOLECULAR COLLOIDS, MUTIMOLECULAR AND MICELLES
Macromolecular Colloids
Macromolecules have large molecular masses. These on dissolution in a suitable solvent form a solution in which the size of the macromolecules may be in the colloidal range. Such systems are called macromlecular colloids. These colloids are quite stable and resemble true solutions in many respects.
Examples of naturally occurring macromolecules are starch, cellulose, proteins and enzymes. Examples of man–made macromolecules are polyethene, nylon, polystyrene, synthetic rubber etc.
Multimolecular Colloids
When on dissolution, a large number of atoms or smaller molecules of a substance aggregate together to form species having size (with diameters less than 1 nm) in the colloidal range, the species thus formed are called multimolecular colloids. For example, sulphur sol consists of particles containing a thousand or more of S8 sulphur molecules.
Associated Colloids (Micelles)
There are some substances which at low concentrations behaves as normal, strong electrolytes but at higher concentrations exhibit colloidal behaviour due to the formation of aggregated particles. The aggregated particles thus formed are called micelles. These are also known as associated colloids. The formation of micelles take place only above a particular temperature called kraft temperature (Tk) and above a particular concentration called critical micelle concentration (CMC). On dilution, these colloids revert back to individual ions. Surface active agents such as soaps and synthetic detergents belong to this class. For soaps, the CMC is ~10-4 to 10-3 molL-1. These colloids have both lyophobic and lyophilic parts. Micelles may contains as many as 100 molecules or more. As the size of the particle increases, Brownian movement becomes slow. Ultimately, when the dispersed particles become big enough to acquire the dimensions of suspension, no Brownian movement is observed.
EMULSIONS
Emulsions are colloids in which both dispersed phase and dispersion medium are liquids. Emulsion can be broadly classified into two types.
(i) Oil in water emulsions: In this type of emulsions, oil acts as (organic solvent) dispersed phase and water acts as dispersion medium. Some examples of this type of emulsions are milk, vanishing cream, etc. In milk, liquid fat is dispersed in water.
(ii) Water in oil emulsions: In this type of emulsions, water acts as dispersed phase and oil (organic solvent) acts as dispersion medium. Cold cream, butter, cod liver oil etc., are examples of oil emulsions.
Identification of Emulsion
The following tests may be employed to distinguish between the two types of emulsions:
(i) Dye test: Some oil soluble dye is added to the emulsion. If the background becomes coloured, the emulsion is water – in – oil type and if the coloured droplets are seen, the emulsion is oil – in – water type.
(ii) Dilution test: If the emulsion can be diluted with water, this indicates that water is the dispersion medium and the emulsion is of oil – in – water type. In case the added water forms a separate layer, the emulsion is water – in – oil type.
Preparation of Emulsion
The process of making an emulsion is known as emulsification. Emulsion may be obtained by vigorously mixing both the liquids. The dispersed drops at once come together and form separate layers. To stabilize an emulsion, the addition of a small quantity of a third substance known as emulsifying agent or emulsifier is essential. Soaps and detergents are most frequently used as emulsifiers.
The other common stabilizing agents are proteins, gum and agar-agar.
Demulsification
The separation of an emulsion into its constituent liquids is called demulsification. The various techniques applied for demulsification are freezing, boiling, centrifugation, electrostatic precipitation or chemical methods, which destroy the emulsifying agents.
APPLICATION OF COLLOIDS
Colloids including emulsions find a number of uses in our daily life and industry. Some of the uses are given below:
(i) Rubber plating: Latex is a colloidal solution of negatively charged rubber particles. Rubber plated articles are prepared by depositing negative charged particles over the article to be rubber plated by making that article an anode in a rubber plating booth.
(ii) Medicines: Medicines in colloidal form are easily absorbed by the body tissues and hence are more effective.
(iii) Sewage disposal: Colloidal particles of dirt, mud etc. carry electric charge. Hence when sewage water is passed through the plates kept at a high potential, the colloidal particles are coagulated due to electrophoresis and the suspended matter gets removed.
(iv) Purification of water: The precipitation of colloidal impurities present in water can be done by adding certain electrolytes like alum etc. The negatively charged colloidal particles of impurities get neutralized by the Al3+ ions and settle down and pure water can be decanted off.
(v) Formation of delta: River water contains charged colloidal particles of clay, sand and many other materials. Sea water is a very big store – house of a variety of electrolytes dissolved in it. As soon as river water comes in contact with sea water, the electrolytes present in sea water coagulate the suspended colloidal particles which ultimately settle down at the point of contact and thus the level of the river bed rises. As a result, water adopts a different course and delta is formed in due course of time.
(vi) Smoke screen: In warfare, smoke screens are used which are colloidal dispersion of certain substance in the air.
Solved Examples
1. Electricity is passed through a colloidal solution then it is called as
(A) Brownian movement
(B) electrophoresis
(C) electro-osmosis
(D) tyndall effect
Sol. (B)
2. As2O3 sol is
(A) positive colloid
(B) negative colloid
(C) neutral colloid
(D) none of the above
Sol. (B)
3. Cellulose dispersed in ethanol is called
(A) emulsion
(B) micelle
(C) collodion
(D) hydrophilic sol
Sol. (C)
4. Action of catalyst depends on
(A) mass
(B) solubility
(C) particle size
(D) none of the above
Sol. (C)
5. Which of the following is an example of zeolite?
(A) ZSM-5
(B) AgNO3
(C) Mg(OH)2
(D) Co(OH)3
Sol. (A(
7. The function of zymase is to
(A) change starch into sugar.
(B) formation of glucose to alcohol and carbon dioxide.
(C) change starch into malt sugar and dextrin.
(D) change malt sugar into glucose.
Sol. (B)